AGES 2026 is poised to be a pivotal event in driving Africa’s just transition, underscoring the continent’s leadership in developing scalable, sustainable, and economically viable solutions to global challenges. Some highlight pathways are: Transport and e-mobility, water and resilience, waste and circular economy, sustainable agriculture…
The 3rd-5th December expo in Nairobi comes at a pivotal moment for East Africa’s food economy as a part of…
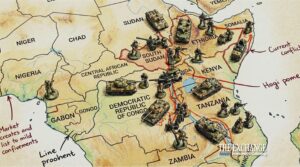
The world looked on with guarded optimism when the foreign ministers of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and…
Binance Junior allows parents to open and manage crypto savings accounts on behalf of their children, enabling young users to…
When the African Union announced Agenda 2063 in 2015, it was touted as Africa’s most ambitious road map yet. It…
In a first of its kind forum between AfDB and African stock…
Featured
Through PPPs, smart financing models, and new policies, Zambia is positioning itself…
Industry & Trade
Through blockchain ecosystem, millions of Africans are getting the opportunity to save…
Countries
The world looked on with guarded optimism when the foreign ministers of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Rwanda signed a historical…
A new HIV prevention drug, lenacapavir, could soon be available for use…
Tanzania President Samia commits to modern railways to revolutionize the economy. Electric…
In its technical document at COP30, Africa raises the issue of forest…
Regional Markets
Resilience, revolution and rivalry have long marked the Horn of Africa, a region that is home to more than 160…
Tech & Innovation
The 3rd-5th December expo in Nairobi comes at a pivotal moment for East Africa’s food economy as a part of a growing regional and continental momentum…
Editor's Picks
Through PPPs, smart financing models, and new policies, Zambia is positioning itself…
Africa
Malawi’s Lazarus Chakwera: “It is only right that I concede defeat out…
Industry & trade
Africa’s gas export potential will be a key agenda at a high-level…
Money Deals
Within the financial history of Africa, the last 10 years have witnessed…
Investing
Viktoria Ventures, a leading pan-African angel investing and early-stage startup support organization,…
Gleichzeitig wie die Entwicklung innovativer Zahlungslösungen wie EPS, entwickelt sich auch die Berichterstattung über Afrikanische Nachrichten rasant weiter. Afrikanische Nachrichtenplattformen bieten wertvolle Einblicke in die wirtschaftlichen, politischen und kulturellen Entwicklungen des Kontinents. Sie bringen Geschichten von Fortschritt, Herausforderungen und Erfolgen aus verschiedenen Regionen Afrikas, die oft in den globalen Medien unterrepräsentiert sind. Durch den Zugang zu diesen Nachrichtenquellen können Menschen weltweit ein besseres Verständnis für die dynamischen Veränderungen und das enorme Potenzial Afrikas gewinnen.
Die Kombination aus modernem Zahlungsverkehr wie EPS und der Berichterstattung über Afrika zeigt, wie Technologie und Information dazu beitragen können, die Welt sicherer, transparenter und vernetzter zu machen.