- AI’s Dual Capacity and a Strategic Opportunity for African Peace and Security
- Africa’s Green Economy Summit 2026 readies pipeline of investment-ready green ventures
- East Africa banks on youth-led innovation to transform food systems sector
- The Washington Accords and Rwanda DRC Peace Deal
- Binance Junior, a crypto savings account targeting children and teens debuts in Africa
- African Union Agenda 2063 and the Conflicts Threatening “The Africa We Want”
- New HIV prevention drug is out — can ravaged African nations afford to miss it?
- From banking to supply chains, here’s how blockchain is powering lives across Africa
Browsing: Agriculture
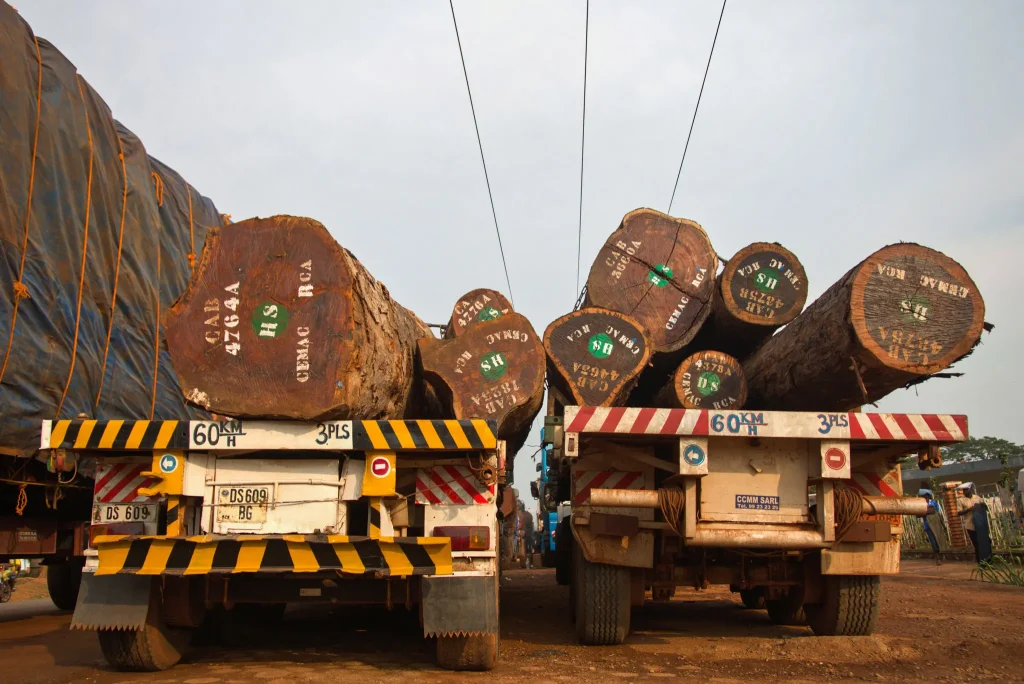
The Central African Republic was the 186th largest exporter in the world in 2020 with a total export value of US$127 million. The country’s exports decreased by US$26.1 million over the past five reported years, from US$153 million in 2015 to US$127 million in 2020.
Rough wood which contributed US$51.9 million in export earnings, gold (US$34.7 million), diamonds (US$14.7 million), sawn wood (US$9.55 million) and refined copper (US$6.66 million) are the most recent export leaders. China (US$50.8 million), the United Arab Emirates (US$37.3 million), Italy (US$12.2 million), Belgium (US$6.84 million), and France (US$4.5 million) are the Central African Republic’s top export markets.
Nations launched the AfCFTA as one of the actions made to support more extensive intra-African trade. The AfCFTA aspires to establish a unified continental market for goods and services. The agreement seeks to harmonise the continent’s various trade liberalization procedures and promote regional integration. Each African nation is a member of at least one of the continent’s approximately 30 bilateral or regional trade agreements.
Africa suffers from marginalization in the global trade system. Nevertheless, the African Regional Trade Agreements heralded a new age of economic integration with significant trade creation impacts. The path to free trade poses several significant obstacles and concerns that African governments must solve.
Africa’s fast population growth exacerbates the issue. According to most estimates, Africa’s population will double by 2050 and then double again by 2100, finally reaching over 4 billion by the end of the century. Feeding Africa’s rising population will need considerable breakthroughs in the continent’s food systems.
However, agricultural progress may be difficult if African farmers are subjected to more severe climatic effects. To prepare for these future difficulties, one must understand how climate change will materialize in Africa and its impact on the continent’s agricultural systems.
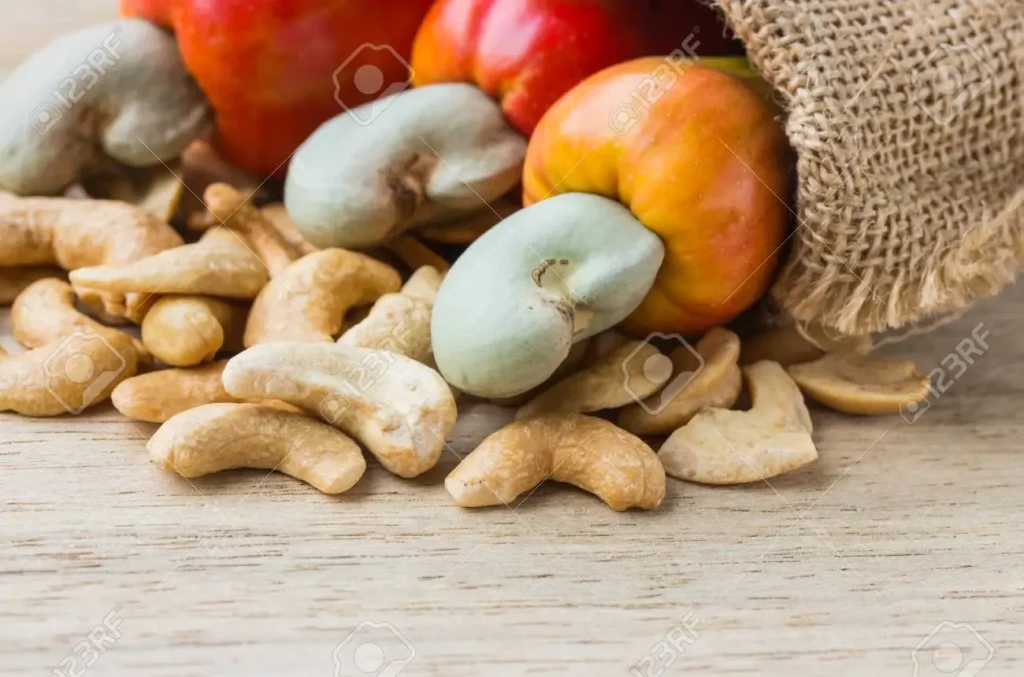
On the backdrop of increasing global demand for cashew nuts, the government of Tanzania is now subsidizing agro-inputs for farmers…
Changes in the global food chain provide essential opportunities to enhance the profile of integrated thinking in Africa. Because these measures will benefit the whole planet, a collective responsibility remains necessary. Landscape-based initiatives and the scaling out of agro-ecological systems and restorative agriculture must be prioritized by African member states.
There should be cross-border collaborations in critical landscapes. Non-African partners and enterprises must also invest in regional systems strategies, focusing on yield and advancing all ecological systems. As investment in Africa’s agricultural industry grows, steps must be taken to avoid negative environmental consequences.
Everyone wants to live in a world with a healthy planet and people and planet. In Africa, this means people with access to healthy diets, economic growth, and development possibilities while interacting with the continent’s unique natural environments.
The summit that will be held from Tuesday, July 19, until Friday, July 22, will focus on economic recovery post-COVID-19…
Africa’s role in the world economy derives from its economic importance to the rest of the world in international trade and as a destination for international investment. Africa has recently become home to the largest free trade area in the world, both by area and by the number of countries.
As economies have been hard hit by the Covid-19 pandemic, the Africa Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) holds economic promise for the continent. The AfCFTA comprises 55 countries with a population of 1.3 billion and combined GDP of about $3.4 trillion. Business leaders and observers regard economic and regional integration as essential for accelerating Africa’s manufacturing, e-commerce, and digitization to reduce an over-reliance on imports, especially from China.
However, there is still much more to do as major components of the agreement still must be negotiated, between many countries and regional economic communities. Moreover, according to the IMF, removing non-tariff barriers could be up to four times more effective in boosting trade than tariff reductions.
Dangote also plans to launch an oil refinery that would produce 650,000 barrels per day. Currently, the Dangote Group is the second-largest employer in Nigeria after the federal government, and a new plant is a tremendous opportunity to replace Russian fertilizer imports with African jobs that create warehousing, transport, and logistics infrastructure that help to reduce poverty.
Global wheat, sunflower, and oil crude prices have soared to unprecedented levels. Africa is heavily reliant on food imports from both countries, and the Continent is already experiencing price shocks and disruptions in the supply chain of these commodities.
Over the past decade, the Continent has seen growing demand for cereal crops, including wheat and sunflower, which has been mainly supported by imports than local production. Africa’s wheat imports increased by 68 per cent between 2007 to 2019, surging to 47 million tonnes.
Uganda to resume sugar imports into Tanzania Kenya is yet to allow the proposed import of 90000 tonnes of Ugandan…
East Africa’s economy is booming, with yearly GDP growth trending upward. The region’s GDP was expected to grow by roughly 5 per cent by 2020. Despite the Covid-19 epidemic, the region increased by 3 per cent in 2021 and is expected to increase to 5 per cent in 2022.