- AI’s Dual Capacity and a Strategic Opportunity for African Peace and Security
- How African economies dealt with the 2025 debt maturity wall
- Africa’s Green Economy Summit 2026 readies pipeline of investment-ready green ventures
- East Africa banks on youth-led innovation to transform food systems sector
- The Washington Accords and Rwanda DRC Peace Deal
- Binance Junior, a crypto savings account targeting children and teens debuts in Africa
- African Union Agenda 2063 and the Conflicts Threatening “The Africa We Want”
- New HIV prevention drug is out — can ravaged African nations afford to miss it?
Browsing: Financial Inclusion
For millions of households in Uganda, remittances play a vital role in safeguarding food security, healthcare, savings and investment opportunities. …
Today, many Africans struggle to manage their finances, often using up their salaries before they even receive them. This struggle…
Financial knowledge remains paramount in an era in which increasingly complex financial products have become readily available to many. Governments in different countries have put more effort into expanding access to financial services. Consequently, the number of individuals with bank accounts and access to credit products is increasing.
Financial literacy remains crucial to personal and economic empowerment, enabling people to make sound financial choices and manage their finances effectively. Africa suffers from a significant shortage of financial literacy, which hinders its economic growth and development.
When CBDCs first came to the fore, many touted such a move as a game-changer in digital finance. Many had thought that the adoption of CBDCs in Africa would take the shape of the adoption of cryptocurrencies, where the region leads in many aspects. However, challenges remain. Lack of the requisite infrastructure, low levels of financial literacy, and operational and regulatory challenges have combined to contribute to low penetration and adoption rates for CBDCs.
The lack of adoption is a current failure point for many launched CBDCs. Nigeria’s eNaira had a million customers one year into its launch, a smattering of its 221 million population. The real challenge of CBDCs lies in developing a clear sense of purpose. African central banks must answer to the kind of role that CBDCs will play in the economy and financial systems.
Financial technology has become an important support for the development of countries around the world. Digital technology, data resources, and…
An efficient crypto mining industry can generate more job opportunities in Africa as the demand for miners, blockchain specialists, and technology specialists increases, . This encourages nations to enhance their energy and technological capacities to support crypto operations. These enhancements can considerably benefit other industries and the economy as a whole.
African nations must embrace the chance to become a crypto mining hub. This can aid in the digital economy’s growth, citizens’ financial standing, and the infrastructure for energy production. Consequently, African governments can invest in cryptocurrencies to acquire alternative funding sources for developing renewable and alternative energy sources.
Regionalising the power balance between central and commercial banks can address the risks associated with the adoption of CBDCs in Africa. Commercial bank digital wallets can thus reduce the costs underlying the correspondent banking channels. These wallets can also promote cross-border trade in Africa by restricting the focus of central banks to the B2B and interbank payment ecosystems. Central banks have traditionally managed this well while incorporating these systems across borders. In such a scenario, each actor—public and private—does what it does best.
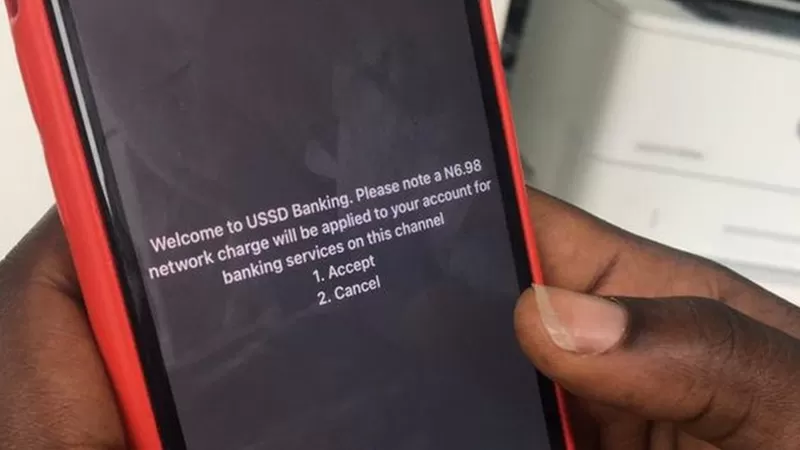
As far back as June 28, 2017, This Day Live said another point to note is that USSD is very important within emerging economies, where the cost to access data services is increasing. Despite the growth of smartphone penetration and 3G/4G coverage, the data access cost is a key factor in deciding how information is consumed.
Meanwhile, the continued reliability of USSD will enable mobile service providers and financial institutions more opportunities to satisfy new market segments, add more value to the customer, and meet underserved customer needs.
In a related article by Myriad Connect published January 29, 2018, the core benefit of USSD is that it doesn’t rely on a data connection to operate, thereby helping reach the billions of people in areas where network coverage is at its most basic or for sectors of the population for whom a data connection is too expensive to access.
So long as a phone can make a call and send a text, then the technology is good to go.
Nigeria’s Access Bank and the United States International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) have signed a commitment letter for a $280 million financing to assist in tackling the gap in financing for small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
In Nigeria, where an estimated 38 million people, or 36% of adults, remain financially excluded, the government has set a target of 95% financial inclusion by 2024.
While this may seem like an ambitious goal, that will require institutions to re-strategize initiatives and policies to accelerate the delivery of financial inclusion services, a lot of tech-backed firms are being developed in the West African country to help achieve this goal.
Among them is Lagos-based FinTech unicorn Interswitch which seems to have heeded that call, leveraging its position as a market leader in digital payment services to bridge the massive financial inclusion gap and help bring as many people into the financial and economic fold as possible.