Africa has stumbled headlong into what has been called the ‘perfect storm’’. From the heavy burden of debt servicing, the instability created by election cycles, geopolitics and war as well as the lingering threat of food insecurity caused by conflict and adverse weather conditions. Seemingly, the proverbial pandora’s box of horrors has been let ajar and the evils through different manifestations are ravaging the continent from all corners. However, as the Greek myth holds, only one thing is said to have been left in the box after it was shut; hope. Amid all the daunting troubles Africa is facing, hope for a better and prosperous Africa is the fuel to help the continent weather these ominous challenges.
We explore some of these existential challenges and some plausible solutions thereof.
Political Instability in Africa
Africa is no stranger to political instability and civil unrest which has stagnated most economies and impeded development. In addition, terror groups like Boko Haram and Al-Shabaab have aggravated the problem, greatly fueling political instability across many African nations. Libya has been in political turmoil for a decade since the ousting of Colonel Muammar Gaddafi while the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has been battling a resurgent M23 rebels. Some of the countries ranked as the poorest in the world, have gained this status due to political instability.
Photo/TRT World
How Can Africa Overcome Political Instability?
- Upholding democracy
- Elections in Africa are often rife with uncertainty and risk of electoral malpractice and violence. As much as many nations claim to be democratic, it’s a façade of a democracy as opposed to a substantive one. However, if democratic values are upheld and followed to the letter, it could largely quell election-related instability in the continent. A number of countries in Africa are under the rule of authoritarian regimes who in a bid to cling onto power have instigated constitutional reforms, to prolong their stay at the helm of power some initiating the postponement of national elections to further their agenda.
- Rooting out Corruption
Corruption is a key instigator of political instability across many African nations. This wound has deleterious effects and perpetuates a cycle of poverty among ordinary citizens, and the rich or elites keep getting richer in many countries. Such a state always triggers rebellion as was seen in the Arab Spring in North Africa. Endemic corruption has been rife during many election seasons where electoral results are manipulated Stemming corruption would go a long way in curbing political upheavals in the continent.
Geopolitics and War in Africa
In a rapidly evolving multipolar world and shifting geopolitical landscape, Africa has come under the radar of rising global powers. How can Africa navigate this landscape and not become a pawn in these emerging geopolitical wars? The so-called new scramble for Africa presents an opportunity that the continent needs to act upon by strategically positioning itself to benefit from partnerships with China, Russia, U.S, U.K, Japan, France and other emerging superpowers. A rule of thumb that Africa should observe should be to avoid aligning itself with a singular power as this would limit its possibilities in the new world order.
Photo/Twitter
How can Africa effectively Service its debts?
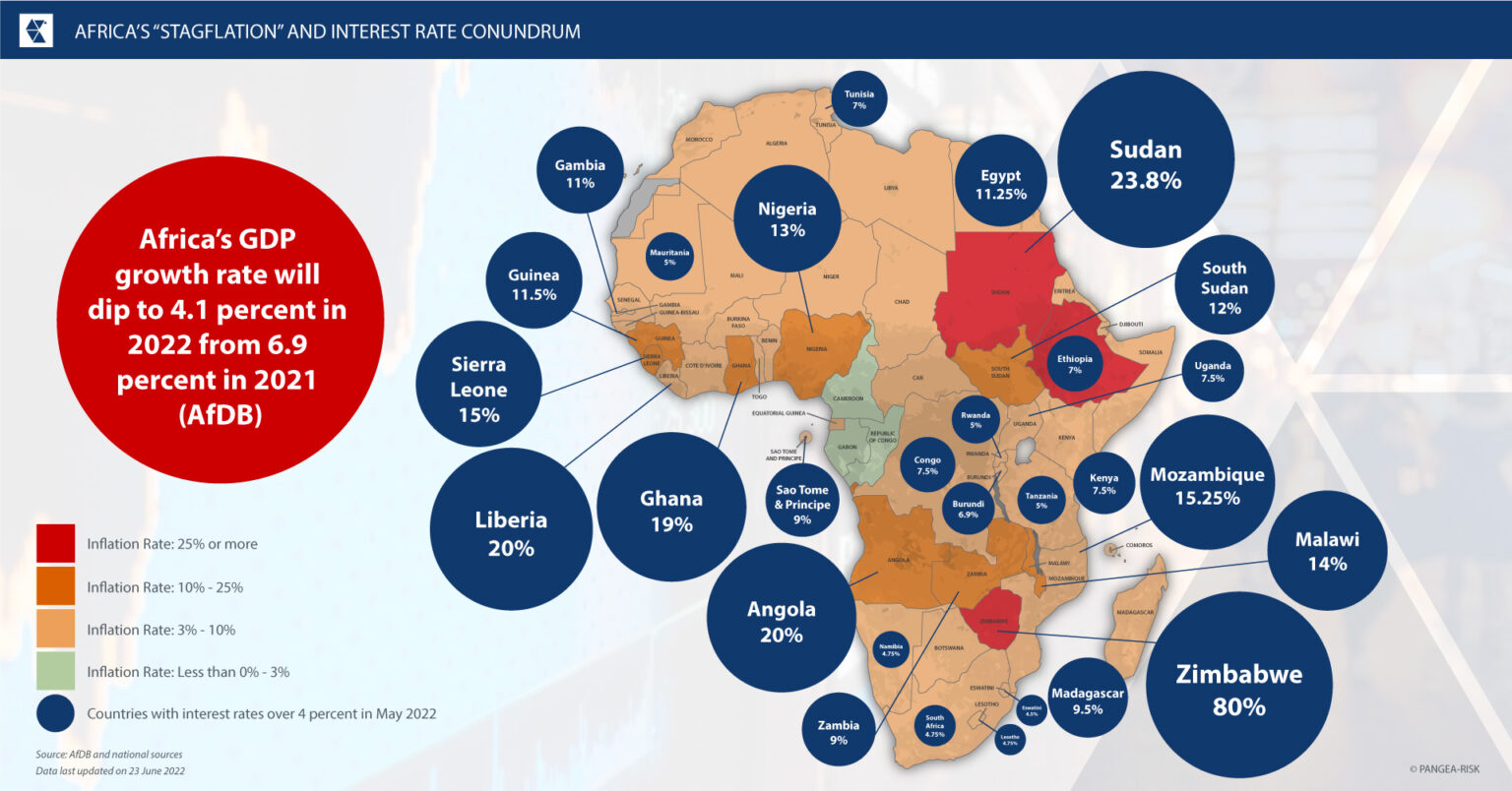
Many African countries are crippling under the weight of hefty sovereign debts forcing countries such as Ghana to defer loan obligations while others are on the brink of debt distress. The ongoing conflict has disrupted the global supply chain of food and fuel, which has caused the worst recession in more than half a century. According to Fitch Solutions Africa’s average inflation rate is at 22.1 percent in 2022, due to the spike in global oil prices.
How can Africa settle these existential debts? Some vital areas that could bring in revenues include:
- Africa should leverage on its natural resources -‘Dash for Africa’s Gas’
- Exploit its Carbon credit market.
- Take advantage of its position as a green energy hub.
- Activate the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
- Capitalize on becoming a fertilizer hub.
Overcoming Food Insecurity
- Africa’s state of food security has been alarming fueled by climate-induced natural disasters. According to the World Bank’s 2022 Global Report on Food Crises 2022 Mid-Year Update, at least one in five Africans goes to bed hungry and an estimated 140 million Africans face acute food insecurity. The Horn of Africa has suffered persistent drought and famine, which had been preceded by a plague of desert locusts whose wave of destruction swept across the food baskets of the region. In addition, food insecurity was aggravated by the Covid-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine war the two largest exporters of wheat and sunflower oil to Africa.
Some ways that Africa can mitigate this challenge include.
Inculcating Science and Technology and Innovation (STI) in Agriculture-Increased investments in Agritech
Agriculture is inarguably a mainstay in most African economies, contributing an average of 30 to 60 percent of GDP, 30 percent of the value of exports and providing employment to about two-thirds of the continent’s working population. Investments in Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) will enable technology adoption in agriculture. The AU Science, Technology and Innovation Strategy for Africa 2024 (STISA-2024) places science, technology and innovation at the epicenter of Africa’s socio-economic development and growth.
Widespread Adoption and Promotion of GMOs
The widespread adoption of Genetically Modified (GM) Foods in Africa could help mitigate food insecurity. Many African countries have been reluctant to adopt GMOs due to myths revolving around health risks. However, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), GM foods currently available on the international market have passed safety assessments, and do not present risks to human health. Some of the advantages that African farmers can reap from GM crop farming include: reduced production costs, increased yields and higher income.
Some African countries such as Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa, Ethiopia, Eswatini and Sudan; are producing GM crops such as drought-tolerant maize, herbicide-tolerant rice, insect-resistant cowpeas among many others.
Also Read:https://theexchange.africa/industry-and-trade/kenyas-gmos-adoption-corporate-engineered/
Manufacturing and Production of Fertilizers
Africa could attain food security by manufacturing and producing its own fertilizers. The African Fertilizer and Agribusiness Partnership (AFAP), estimates that over 40 per cent of African soils face nutrient depletion, partly because of a failure to apply sufficient levels of fertilizers. The AfDB had sounded warning that fertilizer shortages, could lead to a 20 percent decline in food production on the continent. The spike in prices coupled with shortages caused by the Russia-Ukraine war has served as a wake-up call for Africa to produce its own fertilizers. Steps to address this shortage are being taken in countries such as Nigeria where Aliko Dangote is setting up a $2.5B plant while others in Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria have ramped up production. Furthermore, the construction of other plants is underway to meet the high demand in the global markets such as the world’s largest 4.6B ammonia plant in South Africa.
Climate Crisis in Africa
The climate crisis has proved detrimental to African countries, yet the continent contributes the least greenhouse gas emissions in the world at a paltry 4%. The myriad natural disasters experienced across the continent stand testament to the gravity of the crisis. How can Africa mitigate the climate change challenge?
-
Making the Green Transition – Adopting Renewables
Keeping greenhouse gas emissions to a minimum is the key to combating climate change. Adopting renewable sources of energy as opposed to non-renewables is a critical step towards mitigating the climate crisis. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewables which comprise of solar, wind, geothermal energy and hydropower; can make up four-fifth of the continent’s power generation capacity by the end of the decade. Solar energy is highly recommended, to combat climate change as its carbon free. In addition, green hydrogen is gaining prominence as a renewable source of energy.
Read:https://theexchange.africa/industry-and-trade/africas-perfect-energy-cocktail-for-power-sufficiency/
-
Climate Financing – Acquiring Green bonds.
Unlocking finance is paramount to achieving the set African Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), hence the need for innovative approaches to attract and steer financial flows consistent with a country’s NDCs. Green bonds are innovative financial instruments that raise funds for climate resilient and environmentally aligned sustainable development projects, in accelerating climate change mitigation and adaptation. This spans from renewable energy infrastructure, low-carbon transportation, sustainable buildings and other eco-friendly industries.
The goal of the green bond market is to promote and amplify the important role that financial markets can play in helping to address the global climate change crisis. By explicitly specifying the environmentally beneficial projects to which the bond proceeds are allocated, green bonds allow investors to assess and allocate capital to environmentally sustainable investments. More issuance of green bonds will help Africa make the green transition and mitigate the climate crisis.
-
Climate Financing – Acquiring Blue Bonds
As Africa continues to industrialize leading to urbanization, the rate of pollution of its water bodies has gone up. The status quo of most African water bodies undoubtedly beckons for blue bond financing to assist in restoring them to their former state for future posterity. A blue bond is a relatively new form of a sustainability bond, which is a debt instrument that is issued to support investments in healthy oceans and blue economies. Earnings are generated from the investments in sustainable blue economy project.