- AI’s Dual Capacity and a Strategic Opportunity for African Peace and Security
- How African economies dealt with the 2025 debt maturity wall
- Africa’s Green Economy Summit 2026 readies pipeline of investment-ready green ventures
- East Africa banks on youth-led innovation to transform food systems sector
- The Washington Accords and Rwanda DRC Peace Deal
- Binance Junior, a crypto savings account targeting children and teens debuts in Africa
- African Union Agenda 2063 and the Conflicts Threatening “The Africa We Want”
- New HIV prevention drug is out — can ravaged African nations afford to miss it?
Browsing: Sub-Saharan Africa
It remains uncertain how long this economic downturn lasts or which businesses and investors will remain standing when it ends. Nevertheless, many tech startup players believe that the African digital ecosystem will remain relatively unscathed.
This moment provides a chance for Africa-focused funds to flourish. The African tech startup industry offers the funds tremendous possibilities to invest at a low cost. The best businesses find footing at times like these.
When the United Nations General Assembly voted overwhelmingly on March 2 to condemn Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, African countries accounted…
The African logistics market has proven itself ahead of the curve in many areas, with endless potential and opportunities lurking just beneath the surface.
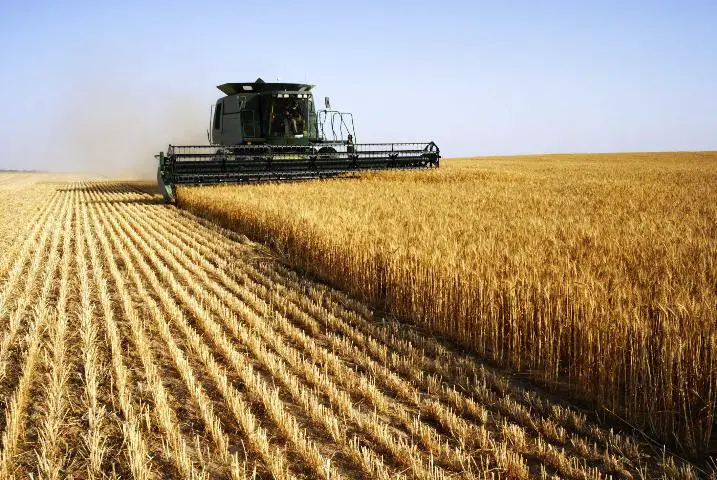
Rising costs have remained a critical issue in the aftermath of the outbreak. Data from the World Bank/NBS Nigeria – COVID-19 National Longitudinal Phone Survey 2020 reveals that food prices rose rapidly following the pandemic. In March and April, basic food commodity prices increased by 17.2 per cent and 18.37 per cent, respectively. According to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), the rise remains the highest in two years.
Recent findings based on comprehensive and long-term monthly food price data have revealed considerable price rises for all chosen food categories during the pandemic. Imported rice and wheat costs, for example, have climbed by 41% and 21%, respectively.
Wheat prices surged by 21% nationally, with considerable increases in price dispersion across markets when the epidemic began, and prices continue to grow.
Wheat is the main component of bread and other products such as noodles, pasta, semolina, and other Nigerian pantry staples. The consumption of these items is higher in cities due to easier market access than in rural regions. Nevertheless, bread remains a major staple throughout the country.
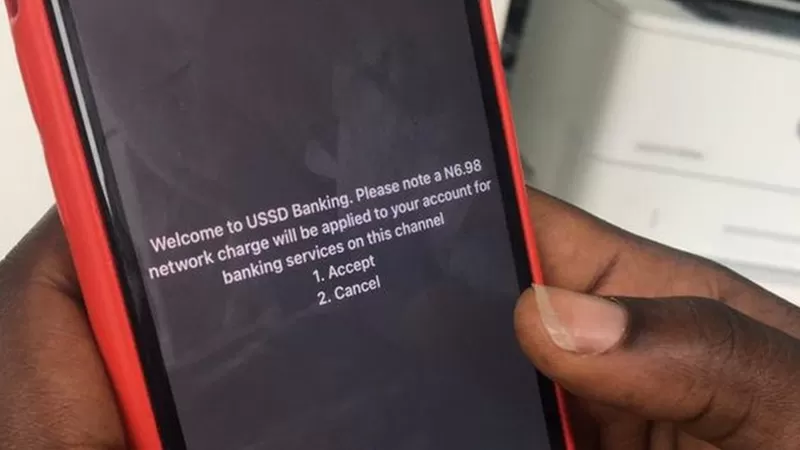
As far back as June 28, 2017, This Day Live said another point to note is that USSD is very important within emerging economies, where the cost to access data services is increasing. Despite the growth of smartphone penetration and 3G/4G coverage, the data access cost is a key factor in deciding how information is consumed.
Meanwhile, the continued reliability of USSD will enable mobile service providers and financial institutions more opportunities to satisfy new market segments, add more value to the customer, and meet underserved customer needs.
In a related article by Myriad Connect published January 29, 2018, the core benefit of USSD is that it doesn’t rely on a data connection to operate, thereby helping reach the billions of people in areas where network coverage is at its most basic or for sectors of the population for whom a data connection is too expensive to access.
So long as a phone can make a call and send a text, then the technology is good to go.
Most African natural gas and oil sources lie in sub-Saharan Africa, including Nigeria, which possesses around one-third of the continent’s reserves, and Tanzania, opportunities Germany should seize.
The proposed Trans-Saharan pipeline would transport gas from Nigeria to Algeria via Niger, traversing a vast, ungoverned area. The proposed pipeline, if built, will connect to the current Galsi, Medgaz, Maghreb-Europe, and Trans-Mediterranean pipelines, which supply Europe from transmission centres on Algeria’s Mediterranean coast.
The Trans-Saharan pipeline would be almost 2,500 miles long. It could send up to 30 billion cubic meters of Nigerian gas to Europe yearly, roughly two-thirds of Germany’s Russian imports in 2021. Unfortunately, the Trans-Saharan pipeline will likely take a decade or more to complete and will face several hurdles as it passes through war and insurgency-ridden areas.
Dangote also plans to launch an oil refinery that would produce 650,000 barrels per day. Currently, the Dangote Group is the second-largest employer in Nigeria after the federal government, and a new plant is a tremendous opportunity to replace Russian fertilizer imports with African jobs that create warehousing, transport, and logistics infrastructure that help to reduce poverty.
Global wheat, sunflower, and oil crude prices have soared to unprecedented levels. Africa is heavily reliant on food imports from both countries, and the Continent is already experiencing price shocks and disruptions in the supply chain of these commodities.
Over the past decade, the Continent has seen growing demand for cereal crops, including wheat and sunflower, which has been mainly supported by imports than local production. Africa’s wheat imports increased by 68 per cent between 2007 to 2019, surging to 47 million tonnes.
Sub-saharan Africa now faces new economic growth challenges, compounded by the Russian invasion of Ukraine A World Bank report estimates…
This as 19 per cent of people in sub-Saharan Africa lived in areas not covered by mobile networks while an additional 53 per cent did not use mobile internet despite having coverage.
The need for accessible internet solutions comes after Meta (formerly Facebook) announced plans to shut down its low-cost Express Wi-Fi internet.
The programme was launched back in 2016 to drive internet connectivity in regions where other forms of connectivity, like ADSL and fibre-optic networks, aren’t readily available or established.
Tanzania’s cement demand is estimated to have clocked 5.9Mt and is growing fast. Maweni Limestone Ltd will be China’s first…