- A dividend is a portion of a company’s profits that is distributed to stockholders.
- The dividend dates include cum dividend date, ex-dividend date, the record date, and the dividend payment date.
- Knowledge about how and when dividends get disbursed helps ensure investors make informed decisions.
Investing in stocks can offer investors a number of benefits, such as the potential for long-term capital appreciation, the ability to diversify their portfolios and the potential for dividend income. Capital appreciation is the increase in the value of an asset over time and stocks can generate long-term capital appreciation if held for the long term. Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across different asset classes or types of investments, which can help reduce overall portfolio volatility. Dividend income is generated when a company pays out a portion of its profits to shareholders, and can provide a steady stream of income to investors.
Well, one important thing to understand is the concept of dividend dates. Knowing the dividend dates can help you understand when to buy and sell stocks so you don’t miss out on any potential profits. Here’s a quick guide to understanding dividend dates and how they can help you become a savvy investor.
What is a dividend?
A dividend is a payment made by a corporation to its shareholders, usually from its profits. It is the portion of profits that a company pays out to its shareholders, and is usually paid on a quarterly or annual basis. The size of the dividend is determined by the company’s board of directors and is typically based on how much profit the company has earned and how much money the company needs for future operations or investments. Dividends can be paid out in the form of cash, stock, or other assets such as property. Dividends are often seen as a way for companies to reward their shareholders for their loyalty and investment in the company. They also help to increase the overall value of a company’s stock by providing a regular return on investment. (https://www.propertyspecialistsinc.com/) Dividends can be taxed at different rates depending on the country and type of dividend, which can affect the amount of money shareholders receive.
Here is an example of a dividend payment. A company declares a dividend of $2 per share, meaning that each shareholder will receive $2 for each share they own. If a shareholder owns 100 shares, they will receive a total of 0 in dividend payments. (casadelninobilingual.com) The company will pay out the dividend to shareholders at a specific date and time, and the payment will typically be made via direct deposit.
Dividends can be classified into two main types: cash dividends and stock dividends. Cash dividends are payments to shareholders in the form of cash, usually from a company’s profits. Stock dividends, on the other hand, involve issuing additional shares of the company’s stock instead of cash payments. In both cases, the dividend is usually paid in proportion to the number of shares held by the shareholder.
Dividend dates explained
When it comes to investing in stocks, understanding dividend dates is an important part of the process. Dividends are a way for companies to reward their shareholders by sharing profits with them. Knowing when dividends are paid out and what type they are can help investors make more informed decisions about their investments.
For example, OK Zimbabwe declared an interim dividend of 0.13 US cents per share, to be paid out of the profits for the half-year ended September 30, 2022. The announcement date was December 21, 2022, last date to trade cum-dividend (January 3, 2023), share trade ex-dividend (January 4, 2023), last record date (January 6, 2023), and payment date (January 20, 2023).
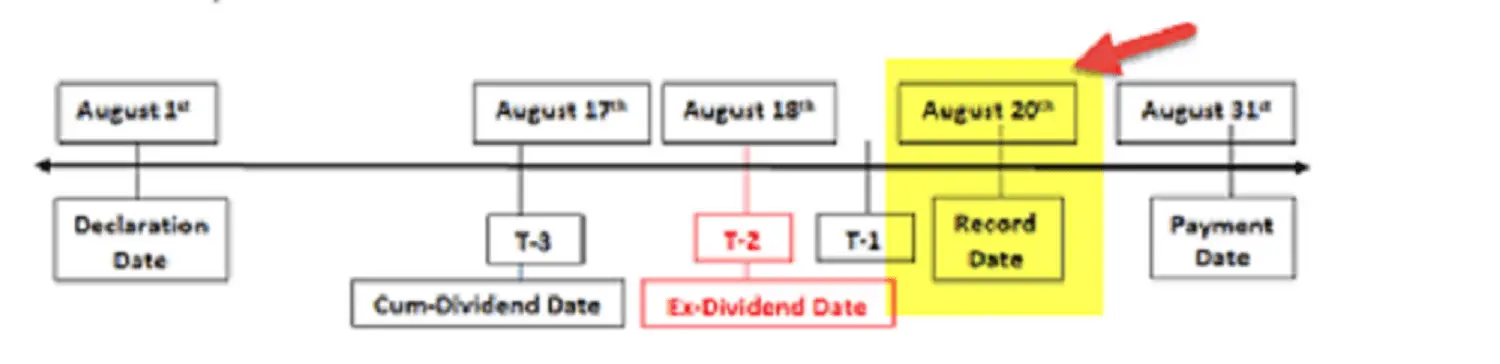
Declaration date/Announcement date
A dividend declaration date is the date on which a company announces that it will pay out a dividend to its shareholders. This date marks the beginning of the process of distributing dividends and is followed by the record date and the payment date. On the dividend declaration date, the company will announce the amount of the dividend and the payment date, as well as any other relevant information.
Cum dividend date
Cum dividend date is the date on which a stock is still eligible for a dividend payment. This date marks the last day that a shareholder must own the stock in order to receive the dividend. Once the stock goes ex-dividend, holders of the stock at that time will no longer be eligible for the dividend payment. The cum dividend date is typically one business day before the ex-dividend date
Ex-dividend date
The ex-dividend date is one business day before the record date, which is the cut-off date for shareholders to be present on the company’s books to be eligible for a dividend payment. The ex-dividend date is an important date to be aware of as any purchase of the stock made on or after this date might mean a late settlement that doesn’t show on the record date.
Record date
The record date is the date on which a company keeps a record of who is eligible to receive the dividend. This date is typically two business days after the dividend declaration date, and one business day before the ex-dividend date. On the record date, the company will keep a record of all shareholders who are eligible to receive the dividend.
Payment date
The dividend payment date is the date on which a company will distribute the dividend payment to its shareholders. This date is typically two to three weeks after the record date, which is the date on which the company keeps a record of who is eligible to receive the dividend. On the payment date, the company will make the dividend payment to all shareholders who owned the stock on the record date.
Understanding these key details about how and when dividends get disbursed helps ensure investors make informed decision about their portfolio management strategy as well as maximize potential return opportunities accordingly.











