- Africa’s new dawn: the rising role of digital and AI in agriculture
- Can Dangote Refinery Transform Africa Energy Ambition
- Gallup Survey: 80 per cent of Kenyan Workers Are Disengaged and Seek New Opportunities
- Madagascar Man Freed from 5KG Tumor After 15-Year Struggle
- How women in Africa are perceived and treated
- Sugar consumption in Kenya to Increase to 1.23 Million Tonnes
- Can Somalia and Turkey Oil deal Bring Change in Somaliland
- Remittances to Kenya dropped to $371.6 million in June, marking a six month low
Regional Markets
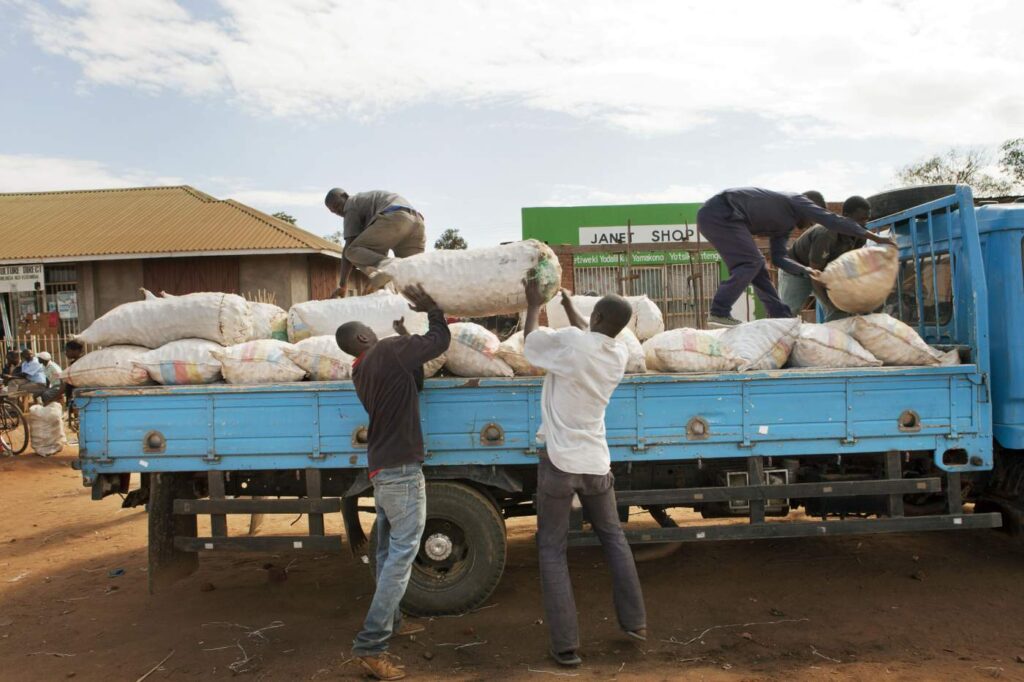
- Under a new COMESA programme, farmers in the five East African countries are expected to access quality seeds, and training on how to improve production and distribution.
- The five-year programme is expected to help the countries cut post-harvest losses in horticulture to 40 per cent or lower, from highs of 60 per cent, for instance in Kenya.
- Agriculture is estimated to contribute on average 27% of the gross domestic product (GDP) in the EAC and accounts for the highest share of employment not only in the region but across Africa.
Agriculture is the backbone of nearly all East Africa region’s economies and the main economic activity for more than 70 per cent of the population. It is estimated to contribute on average 27 per cent of the gross domestic product (GDP) in the EAC and accounts for the highest share of employment not only in the region, but the African.…
- East Africa’s economic growth is projected to grow at 5.3 and 5.8 per cent in 2024 and 2025-26, respectively.
- The World Bank projects African economies to grow by 3.4 per cent in 2024.
- However, faster and more equitable growth is needed to reduce poverty.
East Africa’s economic growth to lead the continent
Economies in East Africa are expected to spearhead growth in Sub-Saharan Africa this year amid increased private consumption and declining inflation, which are supporting an economic rebound in the region.
The World Bank’s latest Africa’s Pulse report indicates the East African Community is projected to grow at the fastest pace at 5.3 and 5.8 per cent in 2024 and 2025–2026, respectively, thanks to robust growth in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Kenya, Rwanda, and Uganda.
This is higher than the compounded growth for Sub-Sahara Africa, which, albeit rebounding from a low of 2.6 per cent in 2023, is …
- Kenya is keen on extending its pipeline to Malaba (Kenya-Uganda border), with Uganda expected to construct a link line to Kampala.
- According to the Shippers Council of Eastern Africa (SCEA), Mombasa used to command up to 70% of transit business, but this has decreased to 60 per cent.
- Uganda imports an average of 2.5 billion litres of petroleum annually, valued at about $2 billion, with KPC handling at least 90 per cent of the volumes.
Kenya is courting Uganda in a fresh bid to retain and possibly increase petroleum exports amid increased competition from neighbouring Tanzania. In recent months, East Africa’s economic powerhouse has come under pressure from Tanzania, which is eyeing to tap more transit markets for imports and exports into the hinterland through the Dar es Salaam Port.
In the latest developments, Tanzania has offered to license Uganda National Oil Company (UNOC) to import petroleum products through Dar …
- East Africa’s insurance sector regulators held the 7th Special Meeting of the Executive Committee (ExCo)of the East African Insurers Supervisors Association (EAISA) in Kenya on Friday.
- The East African insurance supervisors have resolved to promote the development of cross-border insurance products and services jointly.
- The members have also agreed to coordinate joint innovation initiatives relating to insurance development in member states.
Joint resolve for East Africa’s insurance sector supervisors
The East African insurance supervisors have resolved to jointly promote the development of cross-border insurance products and services to address the challenges of low insurance uptake and penetration in the region.
The members have also agreed to coordinate joint innovation initiatives relating to insurance development in member states.
Working under the auspices of the East African Insurance Supervisors Association (EAISA), the supervisors, at their 7th Special Meeting of the Executive Committee (ExCo) meeting held in Eldoret, Kenya, also agreed to employ …
- In 2023, a significant investor sell-off led to a $15.5 million (KSh4.2 billion) decline in the Kenya stock market.
- During the review period, Safaricom’s market valuation declined, attributed in part to prolonged and price-agnostic portfolio outflows by foreign investors in favor of dollar-denominated assets.
- Utility Umeme Limited recorded the highest valuation gains throughout 2023, registering an impressive 115.6 percent return.
Nairobi Securities Exchange-listed firms, including Safaricom PLC, British American Tobacco (BAT), and Cooperative Bank, emerged among the top counters experiencing the highest investor sell-off in 2023, a new trading report reveals.
Over the past year, a consistent trend of investor flight led to the Nairobi Securities Exchange (NSE) witnessing a drop of $15.5 million (KSh4.2 billion) in the value of shares traded on the bourse
The 2024 outlook report by AIB-AXYS Africa Investment indicates that despite some firms, such as Safaricom, recording improvements in share prices towards the end …
- Trade tensions within the EAC bloc have intensified lately, with neighboring countries taking adverse actions against each other.
- In the latest development, Tanzania is blocking passenger flights from Kenya Airways to Dar es Salaam, while Burundi has officially closed its borders with Rwanda.
- Elsewhere, Kenya has been pursuing trade deals with the European Union and the United States, leaving regional economies to play catch-up
Heightened trade and political tensions between the East African member states are threatening to erode the gains of a free market and the dividends of a united bloc for a region expected to achieve the fastest growth across Africa this year.
As East Africa increasingly evolves into a focal point for economic growth and development, underlying trade tensions are testing the region’s unity to the fullest. As nations strive to harness the benefits of globalization, differing economic policies and priorities can often strains trade relations defeating …
- East Africa is set to outshine other regions in 2024 growth with Rwanda, Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda posting impressive numbers.
- This year, Africa’s overall growth is forecasted at 4 per cent, a notable increase from 3.3 per cent in 2023.
- These are findings of a new Africa 2024 outlook report by Stears, an economic analysis and data-driven insights provider.
The prevailing economic woes in Kenya are projected to continue in 2024 with persistent currency depreciation and inflationary pressures taking toll on individuals and businesses. This is according to a new Africa 2024 Outlook report by Stears, a Nigeria-based economic analysis and data-driven insights company.
Already, the latest statistics show that the Kenyan Shilling has already breached the 160 mark against the US dollar.
Stears’ 2024 Outlook delves into key African countries, specifically Kenya and the continent’s powerhouse Nigeria, projecting persisting economic challenges for both economies.
he macroeconomic analysis …
- Ethiopia-Somalia port dispute has seen the European Union, the Organisation for Islamic Cooperation and the Arab League declare support for Somalia.
- The deal on the port agreement has rattled a section of Somalians who took to the streets in Mogadishu to protest against the agreement.
- The Horn of Africa, region comprises countries such as Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia, and has long been a strategic crossroads for trade and commerce.
Hundreds of millions of dollars in lost trade deals could be on the line as the Ethiopia-Somalia port dispute intensifies tension across the volatile Horn of Africa region.
Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed and Somaliland’s leader Muse Bihi Abdi signed an agreement granting Ethiopia a 50-year lease on a naval base, effectively allowing access to Somaliland’s Berbera port for commercial marine operations.
As per the Memorandum of Understanding, landlocked Ethiopia was granted the right to utilize facilities in the Gulf …
- This year, ILO report notes that an additional two million workers are expected to be seeking jobs in Africa and across the globe.
- Last year, the global unemployment rate stood at 5.1 percent, reflecting a modest improvement from 2022 when it was at 5.3 percent, accounting for roughly 191 million people.
- Additionally, the global jobs gap and labour market participation rates showed improvement in 2023. However, a new report highlights that beneath these numbers, fragility is starting to emerge.
An additional two million people are projected to be seeking work this year, potentially raising the average unemployment rate in Africa and across the world by about two per cent to 5.2 per cent from last year’s 5.1 per cent.
In its World Employment and Social Outlook Trends: 2024 report, the International Labour Organization (ILO) notes that this trend will accelerate growing social inequalities, a key pain point for policymakers across …