- How South Africa plans to counter the negative impact of Trump tariffs sting
- Africa’s BPO industry enters AI era with 40% of tasks at risk by 2030
- Trump tariffs sting set to ruffle several economies in Africa
- Africa Energy Bank secures key backing from Nigeria, Angola and Ghana
- AIM Congress 2025 gets a boost as International Development Bank signs on as gold sponsor
- African energy: Opportunities and challenges presented by Russia’s investments
- Africa’s smart farming push—a revolution or a mirage?
- BRICS summit in Brazil to focus on global governance reform
Author: Giza Mdoe
Giza Mdoe is an experienced journalist with 10 plus years. He's been a Creative Director on various brand awareness campaigns and a former Copy Editor for some of Tanzania's leading newspapers. He's a graduate with a BA in Journalism from the University of San Jose. Contact me at giza.m@mediapix.com
- Montero Mining and Exploration Ltd has received the final $7M installment of a $27M settlement with Tanzania, resolving a long-standing dispute over the expropriation of its Wigu Hill rare earth project.
- While this payment marks the conclusion of the legal battle, Montero noted that final legal costs and expenses must still be determined before net proceeds can be confirmed.
- The company is now evaluating the distribution of funds and expects to provide an update on potential shareholder payments by Q2 2025.
Montero Mining and Exploration Ltd has confirmed receiving $7,000,000, being the final instalment in a US$27,000,000 settlement between the Company and Tanzania. Paid in cash, the final Instalment brings to an end the long standing dispute between the company and the East African country where it has mining operations.
Notably, the amount accounts for approximately 39 per cent of Montero’s initial $70 million claim in a legal battle that …
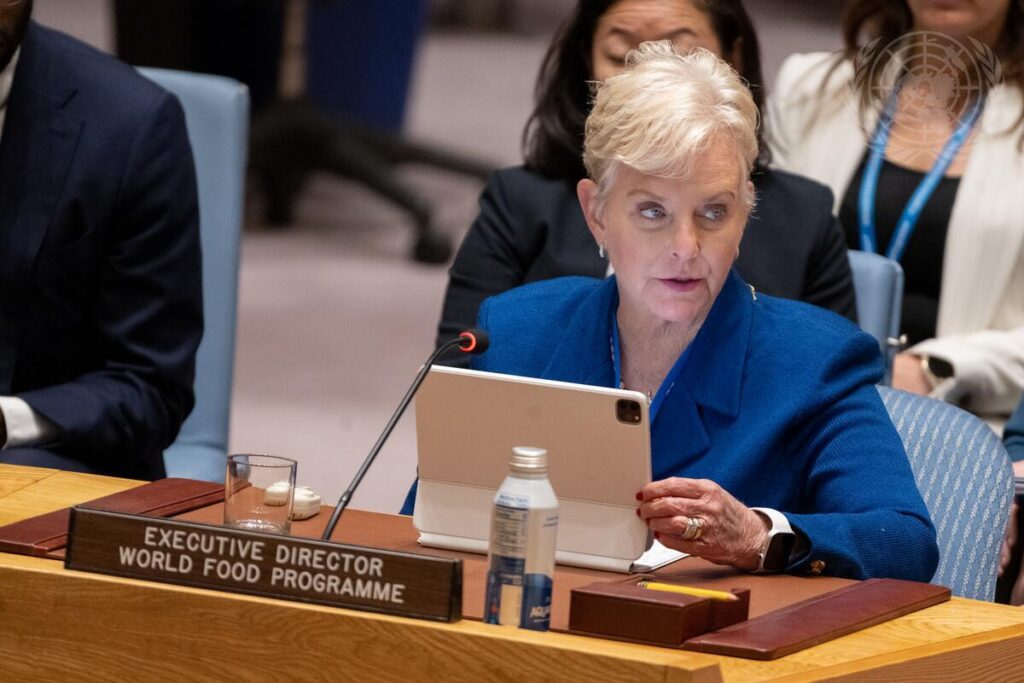
- Trump’s escalating aid cuts are crippling global humanitarian efforts, with the UN’s World Food Programme (WFP) now forced to shut its southern Africa office.
- The closure threatens food assistance for millions, as WFP has been leading the response to the region’s worst drought in 40 years.
- With USAID slashing 90% of foreign aid contracts and WFP facing a 40% budget cut, 26 million people across seven countries are at risk of severe hunger.
The escalating U.S. aid cuts under President Donald Trump are impacting millions worldwide, exposing the extent to which American taxpayers have been funding global aid. This raises a critical question: Is Trump’s decision justified?
His administration’s aggressive push to reduce foreign aid—led by the so-called Department of Efficiency in Government—continues to disrupt operations of major international organizations, with the latest casualty being the UN’s World Food Programme (WFP).
Currently, WFP provides food assistance to over 150 million …
- Tanzania is growing its national gold reserve as a smart move to counter USD shortage.
- Already, the country lags behind peers Kenya and Zimbabwe in gold reserve held yet its a major exporter of the precious mineral.
- Will Tanzania’s new plan be enough to counter its currency woes?
In the face of a persistent U.S. dollar shortage crisis, authorities in Tanzania are turning into gold hoarding as a potential solution. Despite being Africa’s fourth largest gold producer, accounting for 1.3 per cent of the global output, Tanzania’s gold reserves stand at an estimated 45 million ounces, which is relatively low compared to its peers. For context, Kenya holds 0.02 tonnes, Zimbabwe at 2.5 tonnes, while the world’s largest economy and issuer of the dominant dollar, boasts a staggering 8,133.46 tonnes in gold reserves. Will Tanzania’s new plan be enough to counter its currency woes?
For policymakers in Tanzania, storing value …
- Tanzania tourism surpasses 5 million visitor numbers target.
- Data shows the number of Chinese tourists to the East African nation is increasing annually.
- Film featuring top Chinese actor has big impact in Tanzania tourism.
Tourism in Tanzania is growing faster than anticipated with the country having hosted 5.36 million tourists in 2024, a figure higher than the targeted five million tourists by 2025. Tanzania’s Minister for Natural Resources and Tourism, Pindi Chana told a stakeholder’s meeting earlier in the week that the 5 million plus tourists racked in 4 billion U.S. dollars in revenue last year.
Notably, of the said tourists, 3.22 million were domestic while 2.14 million were drawn from international source markets, showing a significant increase in domestic tourism. “These efforts have effectively showcased Tanzania’s breathtaking landscapes and rich cultural heritage, positioning the nation as a desirable travel destination,” said Chana in a statement highlighting the significance of …
- Tanzania well underway to achieve clean energy transition.
- The nation’s success story has been enhanced by Siemens Energy’s investment in Ubungo Power Plant in Dar Es Salaam.
- The technology to drive the energy transition is available, and Siemens Energy says it has capacity to make it accessible.
Tanzania faces two fundamental energy transition challenges, achieving universal access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy services by 2030, as set out in the United Nation´s Sustainable Development Goal 7. The country is also keen on increasing the supply of electricity to fuel economic growth and improve livelihoods while avoiding a lock-in to polluting fossil fuels.
To this end, we spoke to François Xavier Dubois, Head of Business Development for Siemens Energy East Africa about the progress made and the barriers to transition to clean energy in Tanzania. We also explored the significance of gas to power, green hydrogen, and the potential …
- USAID was established in 1961 by US President John F Kennedy.
- The charity arm has over 10,000 global employees and spends $40 million in humanitarian support.
- Trump, Musk allege USAID is run by “radical left lunatics” getting away with “tremendous fraud.”
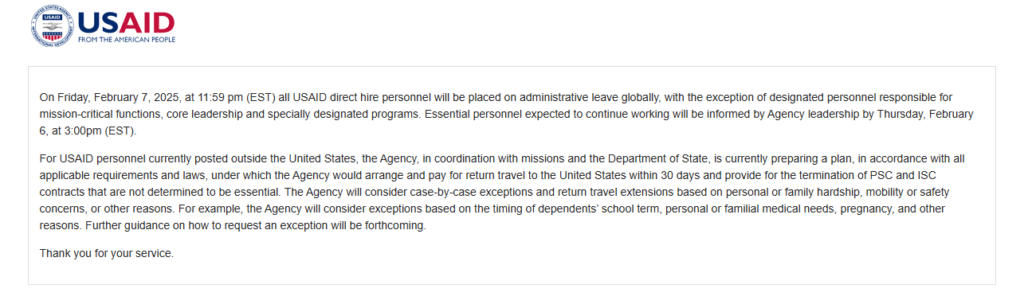
A notice placed on the USAID website that announces to all its global staff, over 10 000 personnel, the commencement of an administrative leave this Friday.USAID, a giant charity arm of the US government is being dismantled by U.S. President Donald Trump. This decision is set to sent shockwaves across the world as it comes after almost a century of USAID operations. Established in 1961 by President John F Kennedy, USAID has over the years assumed a huge role in humanitarian affairs across Africa, but under Trump, the organization is now unceremoniously been drugged through the dirt.
Its over 10,000 employees will either be laid off or reassigned and …
- Donald Trump threatens to cease all funding to South Africa.
- South African-born Elon Musk against Expropriation Law.
- South Africa says the new law is just and seeks land equality in the wake of apartheid.
Donald Trump and his advisor, Elon Musk, have threatened to cease all aid to South Africa over its Expropriation Law. The move comes after South Africa’s President Cyril Ramaphosa signed an Expropriation Bill into law this January a move that does not sit well with Trump and Musk, an American billionaire who was born in South Africa.
South Africa says the law, seeks to empower the state to conduct land expropriation to provide equitable compensation to those who lost their land under the infamous apartheid regime. “The land expropriation law seeks to repeal the apartheid-era Expropriation Act (1975) which saw thousands of African families forcibly removed from their land to benefit the white minority,” explains a …
- M23 rebels reportedly at Kavumu, about 40km north of mineral-rich Bukavu area.
- UN experts claim the M23 rebels – one of over 100 militias seeking control in DRC’s east – is receiving support from about 4,000 soldiers from Rwanda.
- According to Kinshasa, Rwandan soldiers are pillaging valuable resources from the mineral-rich eastern zone of DRC.
As M23 rebels continue pushing deeper into the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) after capturing the mineral-rich city of Goma, the city of Bukavu, the capital of South Kivu province, is on the verge of falling under their control.
Media reports show that M23 rebels are threatening to march to DRC capital Kinshasa as they push the government of Felix Tshisekedi on the negotiating table to meet their demands. “We will continue the march of liberation all the way to Kinshasa,” announced rebel leader Corneille Nangaa on Thursday, four days after the group confirmed the …
- Trump’s deportation list has people from virtually every nation in the world, including Africa.
- Amnesty Internation has protested inhumane treatment of deportees.
- Chains, cuffs, military planes used to ‘criminalize’ immigrants.
Thousands of people from Africa are fast joining Trump’s deportation list, one of the trending topic across all media, following a nationwide US immigration crackdown that resulted in thousands of arrests, the US Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) has reported. US president Donald Trump returned to power on a ‘Mass Deportation’ ticket and he is living up to this eerie promise.
The nearly 1000 arrests per day look overwhelming and could surpass what his predecessor, Joe Biden, carried during the last four years in office. Biden okayed 1.5 million deportations, according to figures by the Migration Policy Institute.
While Biden focused on individuals who had committed crimes, Trump is going for any and all undocumented persons. “Since taking office, Trump …
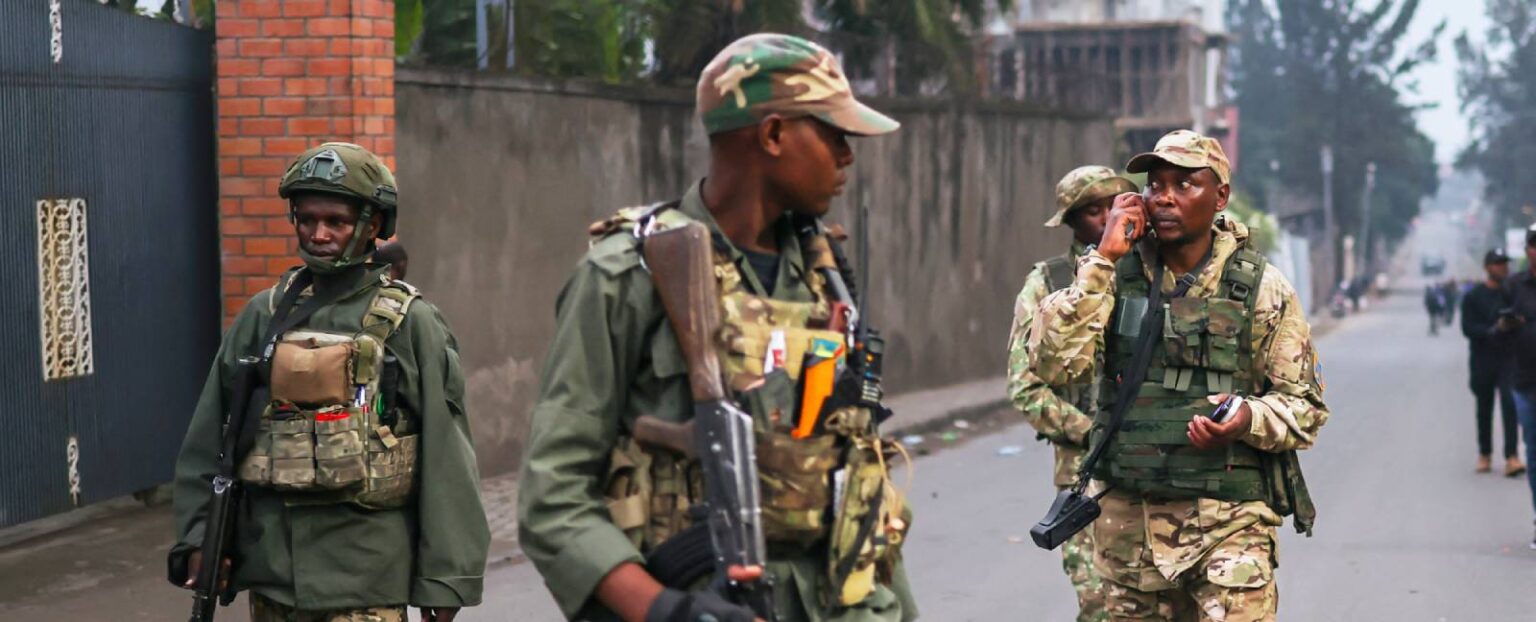
- Rwanda is fighting accusations of backing M23 rebel attacks in Goma, the most strategic city within the mineral-rich eastern DRC.
- Already, the UN and other humanitarian agencies have pulled out non-essential personnel out of Goma.
- Early this week protestors in Kinshasa attacked US, Rwanda, Kenya, Belgian and French embassies, demanding decisive counter against M23 rebels.
The war in Goma has sucked in Rwanda with authorities in Kigali increasingly fighting an avalanche of accusations that the country’s military is invading the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) in concert with the M23 rebels. According to reports from both local and international media, “The Rwandan army is lining up at the [DRC] border, ready to invade,” an anonymous source privy to official on the ground told media.
“Large numbers of troops from Rwanda have been pouring across the border into the Democratic Republic of the Congo to help rebels seize the regional capital …














