- Africa is a continent with a rapidly growing population and a developing economy. However, one of the major challenges that Africa faces is a lack of reliable and accessible electricity.
- Nuclear power generation is one of the options that could potentially solve Africa’s power problems, but it is also a controversial and complex issue.
- Nuclear power plants use heat from nuclear fission to produce steam, which then drives turbines connected to generators to produce electricity.
South Africa has been experiencing a series of constant rolling blackouts for the past few years. While load shedding may have become a norm in the country, it is not the only African country experiencing an energy crisis.
The struggle to keep the lights on is not unique to South Africa and can be described as a Cape to Lagos problem.
Zimbabwean citizens experience power outages that last up to 19 hours a day which might be a reflection of what South Africa might go through if the load shedding is not fixed anytime soon. According to News24, Zimbabwe’s electricity gets turned on between midnight and 5am each day. This means, most households can only prepare food or prepare for the next day’s activities when the clock strikes midnight. According to BBC, businesses have been heavily impacted by the power cuts and some have even opted to run operations such as manufacturing at night, when electricity is available.
What is causing Zimbabwe’s energy crisis? Like many countries trying to adjust and move away from coal power stations, Zimbabwe invested in a hydrogen plant to generate electricity. However, the country is experiencing persistent drought which means the hydro plant at the giant Kariba Dam has low water levels. According to MoneyWeb, the Zimbabwean government is trying to remedy the situation by approaching independent power producers (IPPs) and neighbouring countries to help with generation capacity.
One possible solution to the energy crisis in Southern Africa Power Pool is the increased use of nuclear power. Eskom, South Africa’s state-owned power company, is reportedly weighing the nuclear fuel impact after a US-South Africa pact ends. According to Bloomberg, the Agreement for Cooperation in Peaceful Uses of Nuclear Energy between the US and South Africa expired on December 4, 2022.
This resulted in Westinghouse Electric Co. losing its license from the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission to export fuel-assembly components to Eskom’s Koeberg plant near Cape Town. Bloomberg also reported that Eskom is considering plans to increase its use of nuclear power. However, not everyone is in favor of this solution, as there are concerns about the safety and cost of nuclear power.
The Southern Africa Power Pool (SAPP) is a regional organization that coordinates and manages the interconnected electricity systems of several countries in southern Africa. Its main goal is to increase the stability and efficiency of the regional power grid by facilitating the exchange of electricity among member countries. The organization was established in 1995, and its members include Angola, Botswana, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Swaziland, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Advantages of Nuclear Power Generation
Nuclear power generation is the process of using nuclear reactions, typically nuclear fission, to produce electricity. Nuclear power plants use heat from nuclear fission to produce steam, which then drives turbines connected to generators to produce electricity.
One of the main advantages of nuclear power generation is that it is a clean and efficient form of energy. Nuclear power plants do not produce any greenhouse gas emissions, which means that they do not contribute to climate change. Additionally, nuclear power plants have a high capacity factor, which means that they can produce electricity at a relatively stable and consistent rate. This makes them a reliable source of power for countries with a growing population and economy.
Another advantage of nuclear power generation is that it is relatively inexpensive to operate and maintain. Once a nuclear power plant is built, the cost of the fuel is relatively low, and the plants can operate for up to 60 years. This means that nuclear power generation can provide a long-term and stable source of energy.
Several countries around the world have successfully implemented nuclear power generation as a source of energy. One example is France, which generates over 70 per cent of its electricity from nuclear power. This has allowed the country to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and decrease its greenhouse gas emissions.
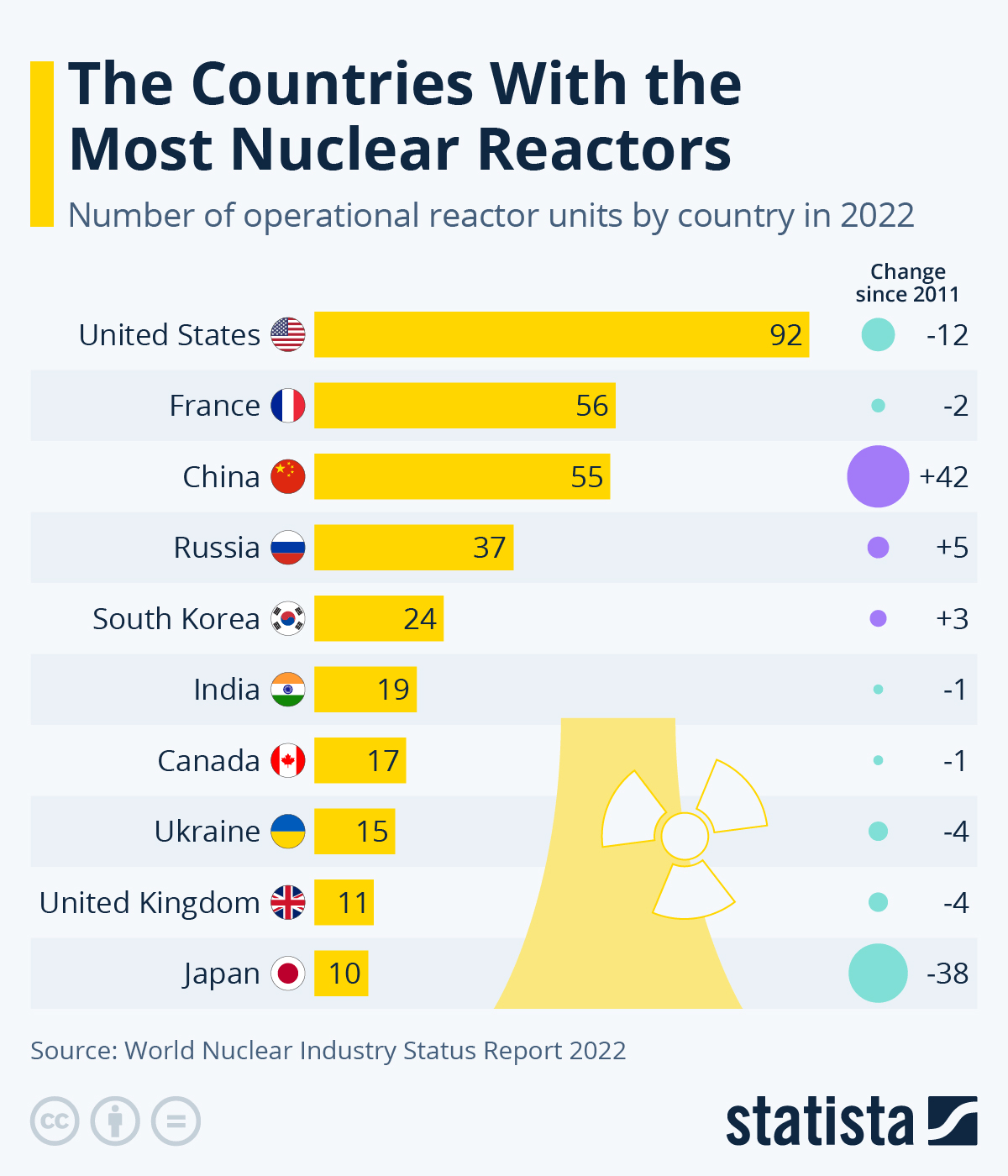
Another example is South Korea, which has the fifth-largest nuclear power generating capacity in the world. The country has successfully used nuclear power generation to provide a stable and reliable source of energy while reducing its dependence on imported fossil fuels. Additionally, Russia has a long history of nuclear power generation, currently it has the largest number of reactors and generates the most electricity from nuclear power in the world. These countries have effectively managed the challenges and risks associated with nuclear power generation through strict safety regulations, regular maintenance, and effective emergency response plans.
Challenges and Risks of nuclear power generation
One of the main challenges of nuclear power generation is the cost of building and maintaining nuclear power plants. Building a nuclear power plant is a complex and expensive process, and it requires a significant amount of investment. Additionally, the cost of maintaining a nuclear power plant requires highly skilled personnel who come at a premium.
Another challenge of nuclear power generation is the risk of accidents and disasters. Nuclear power plants are complex systems that require strict safety regulations and maintenance. However, if an accident or disaster occurs, it can have devastating consequences. This is a major concern for many African countries that do not have the necessary infrastructure and resources to respond to a nuclear disaster.
One of the most well-known accidents in the history of nuclear power generation is the Chernobyl disaster of 1986. The disaster occurred at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine, which was then part of the Soviet Union. A reactor at the plant overheated and exploded, releasing a large amount of radioactive material into the environment. The explosion and subsequent fires caused a release of radioactive particles into the atmosphere, which spread over much of Western USSR and Europe. The disaster resulted in the deaths of two plant workers, and the evacuation of over 350,000 people. The long-term health effects of the disaster, including cancer and other illnesses, are still being studied.
Another example is the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, which occurred in 2011 in Japan. A massive earthquake and tsunami caused significant damage to the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, leading to a failure of the cooling systems and subsequent nuclear meltdowns. The disaster resulted in the release of radioactive materials and the evacuation of thousands of people from the surrounding area. It also caused a widespread loss of power and significant damage to the economy of the region.
Another alternative to nuclear power is the implementation of 100 per cent power backup tariffs, as proposed by Mr. Price, a South African retail company. However, this plan has been opposed by Eskom. Additionally, other alternative energy sources such as solar and wind power are also being considered as potential solutions to the energy crisis.
The energy crisis in Southern Africa is a complex issue that requires a long-term, sustainable solution. While nuclear power may be one option, it is important to consider all alternatives and weigh the pros and cons before making a decision. Ultimately, it is vital to find a solution that will ensure a reliable and stable power supply for all citizens in the region.











