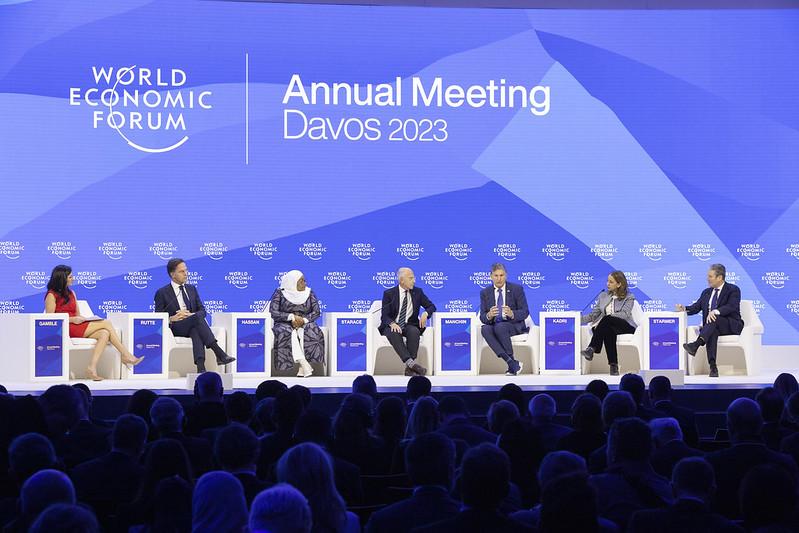
- Tanzania President Samia Suluhu has urged the world to look to Africa for energy amid the climate, energy and geopolitical crises that have been raging for some years now.
- Speaking during the 53rd World Economic Forum Annual Meeting as a session on “Repowering the World” Suluhu said Africa has everything when it comes to energy.
- Africa needs a lot of energy as many Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies are being applied there and a lot of related manufacturing is carried out there.
Tanzania President Samia Suluhu has urged the world to look to Africa for energy amid the climate, energy and geopolitical crises that have been raging for some years now.
Speaking during the 53rd World Economic Forum Annual Meeting as a session on “Repowering the World” Suluhu said Africa has everything when it comes to energy.
“It is time the world looked to Africa for energy. We have everything when we talk about green energy – cobalt, copper, nickel… You can extract and manufacture in Africa, provide energy to Africa and take it to other countries,” she explained.

Making an appeal for greater private sector investment in Tanzania, Suluhu said Africa needs more energy as the continent ramps up manufacturing.
“We want to build regional power pools in East African and Southern African… if any region has a shortage, the other could supply it,” she said. Suluhu added that instead of Europe, Japan or India pursuing unilateral policies, more concerted efforts are needed to tackle the energy crisis that is truly global in nature.
Data from Africa Development Bank, (AfDB) reveals that Africa’s energy potential, especially renewable energy, is enormous, yet only a fraction of it is being currently employed.
Hydropower provides around a fifth of current capacity but not even a tenth of its total potential is being utilized.
Similarly, the technical potential of solar, biomass, wind and geothermal energy is significant.
According to AfDB, over 640 million Africans have no access to energy, corresponding to an electricity access rate for African countries at just over 40 percent, the lowest in the world. Per capita consumption of energy in sub-Saharan Africa (excluding South Africa) is 180 kWh, compared to 13,000 kWh per capita in the United States and 6,500 kWh in Europe.
Access to energy is crucial not only for the attainment of health and education outcomes, but also for reducing the cost of doing business and for unlocking economic potential and creating jobs.
Insufficient energy access manifests itself in hundreds of thousands of deaths annually due to the use of wood-burning stoves for cooking; handicaps the operations of hospitals and emergency services.
Global Energy Crisis
Speaking at the same session, Ilham Kadri, CEO and Chairman of Solvay, a Belgian chemicals company, said, chemistry is the mother of all industries, and it is imperative to create diversified supply chains of metals and rare earths such as lithium, cobalt, nickel and copper that are essential components of EV batteries and so many other applications in the energy transition.
China has built rare earths value chains for decades and to avoid a “Russian gas supply syndrome”, she said Europe and countries around the world must find diversified sources of these metals and minerals as well as localize battery assembly.
From reskilling workers to issuing permits, Europe needs policies that “get it done quicker”, Kadri said, quoting United States’ new Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) that offers funding and incentives to accelerate the clean energy transition and has raised fears in Europe of an investment drain. “Europe must boost its competitiveness to prevent de-industrialization,” she said. “The question is not IRA or not, but what does it take for Europe to have a competitive industrial policy? I need clean energy, at cost and at scale, and 365 days a year.”
In the same vein, Mark Rutte, Prime Minister of the Netherlands, said the IRA is an opportunity for Europe to cut bureaucratic red tape, which would unleash opportunities for innovation, new jobs and working together at a European scale, or else “real action will move to Asia and other parts of the world”.
Asked if Europe overlooked its dependency on cheap Russian gas for too long, Rutte agreed that Europe could have cut this dependence sooner, but added that it was a collective failure, and not just Germany’s, as it is sometimes made out to be. Natural gas will continue to be used as a transition fuel in the short- to medium term, he said, but longer term, the direction is decidedly towards renewables, green hydrogen and even nuclear.
“I would not be amazed if many more countries start to reinvest in nuclear,” he said, adding that Belgium will build two new nuclear reactions.
The Technology Perspective Report of the IRA got a thumbs-up from Francesco Starace, CEO and General Manager of Enel, for not only interpreting the need to transform energy systems but also to transform supply chains and industrial systems. “China and some Asian countries took the chance [to do so] earlier,” he said. The energy transition is taking place much faster than originally estimated, and will accelerate, he said, adding that this puts additional pressure on an industry used to longer time horizons.
The US has significantly increased its gas production to supply the EU, said Joe Manchin III, Senator from West Virginia (D). “Our friends and allies were hurting,” he said, referring to Russia’s curtailment of supplies to the EU, “And we couldn’t come to your rescue fast enough.” He added that the US would continue to ramp up gas production but would do it cleaner than ever while simultaneously investment in carbon capture, methane capture, renewables, storage, and so on. “We will not get rid of something until we have [an alternative] that works at least as well,” he said.
Taking a more measured stance towards fossil fuels, Keir Starmer, Leader of the Opposition of the UK, said his Labour Party supports the use of oil and gas during the energy transition but is against any new investments in fields in the North Sea or elsewhere. “We have a strict target for 2030 for green power,” he said, referring to Labour’s target of 60% renewables in the energy mix by 2030.
Starmer said the British Prime Minister’s absence in Davos was in line with a general failure to grow the economy. “Britain has not had a strategic plan for 10 years, foreign direct investment in the UK is down to 4%,” he said, adding that it is essential to restore trust in institutions and match public investment with private to unlock the UK’s potential.