- Generative AI can create original content such as text, images, and videos.
- As an emerging technology, generative AI does hold transformative potential not only in marketing and the creative arts but also in healthcare, banking, and finance amongst other sectors.
Generative AI has made notable footprints in recent years, beaconing as one of the most recognisable advancements, AI can create original content such as text, images, and videos.
AI fundamentally refers to systems capable of producing entirely new and original content, distinguishing it from other AI applications that primarily analyse existing data for decision-making. These models can generate original written articles, images, audio samples, or video footage based on training from extensive datasets.
Leading models like Gemini, GPT-4, Claude, and Bing AI are renowned for creating remarkably human-like text from given prompts. In contrast, others like Stable Diffusion, Firefly, and DALL-E are known for generating vivid images from text descriptions. These models have undergone months of training on massive datasets containing millions of human-generated examples, enabling them to produce outputs that mirror human creativity in areas they have been exposed to during their training phases.
Potential Generative AI in Kenya
Generative AI’s potential in Kenya is vast, and it’s already beginning to transform the business landscape. For instance, it enables the creation of new, original content, ranging from Swahili poems to visual art that captures the tranquility of a Tsavo sunset. Moreover, it allows businesses to customise outputs that resonate with Kenyan audiences.
As an emerging technology, AI does hold transformative potential not only in marketing and the creative arts but also in healthcare, banking, and finance amongst other sectors. In healthcare, it can diagnose conditions, create clinical documentation, manage reimbursement forms, and assist doctors in treatment planning.
However, medical professionals must guide the development and application of these technologies, prioritising patient privacy and safety over commercial motives. In banking and finance, AI’s capabilities extend to cybersecurity, fraud detection, personalised offers, market trend analysis, and automating customer services. Additionally, these applications are adept at analysing financial data to forecast market trends, offering valuable competitive insights for financial institutions. As the technology advances, it promises significant enhancements in these sectors, potentially leading to widespread improvements in the lives of Kenyans across the country.
Read Also: Artificial intelligence (AI) could create a turning point for financial inclusion in Africa
Generative AI in Business in Kenya

These applications yield tangible benefits, such as superior customer engagement and market leadership. Although being an early adopter of generative AI offers substantial advantages, it is important to remember that this must come with significant responsibility. It’s essential to ensure its development and usage are ethical and inclusive, a challenge Kenya’s tech scene is well-equipped to tackle.
This approach offers businesses the opportunity to lead in the responsible deployment of generative AI, providing long-term benefits.
Notably, adopting generative AI is a continual process, requiring staying informed about trends and ethical considerations. By actively contributing to a responsible, generative AI-driven future, Kenyan businesses can keep pace with technological advancements and shape the evolution in ways that benefit both consumers and businesses.
Innovative solutions via Generative AI
Gaining a competitive edge will ultimately come from broadly envisioning how generative AI can elevate businesses.
It’s not just about reducing costs; the technology also unlocks new possibilities for instance, offering micro-personalised services and creating innovative solutions tailored to the specific needs of Kenyan consumers. What’s clear is that as long as the unique strengths and weaknesses of generative AI are kept in perspective, Kenyan businesses can responsibly tap into its lucrative potential as part of their digital transformation initiatives.
The rapid maturation of this technology warrants dedicated strategies led by C-suite executives. Generative AI represents the next frontier for efficiency, revenue, and differentiation gains for Kenyan firms ready to embrace emerging technologies. With sensible implementation, the technology could very well prove to be the tipping point leading to sustainable competitive advantages.
Concerns in the Adoption of AI
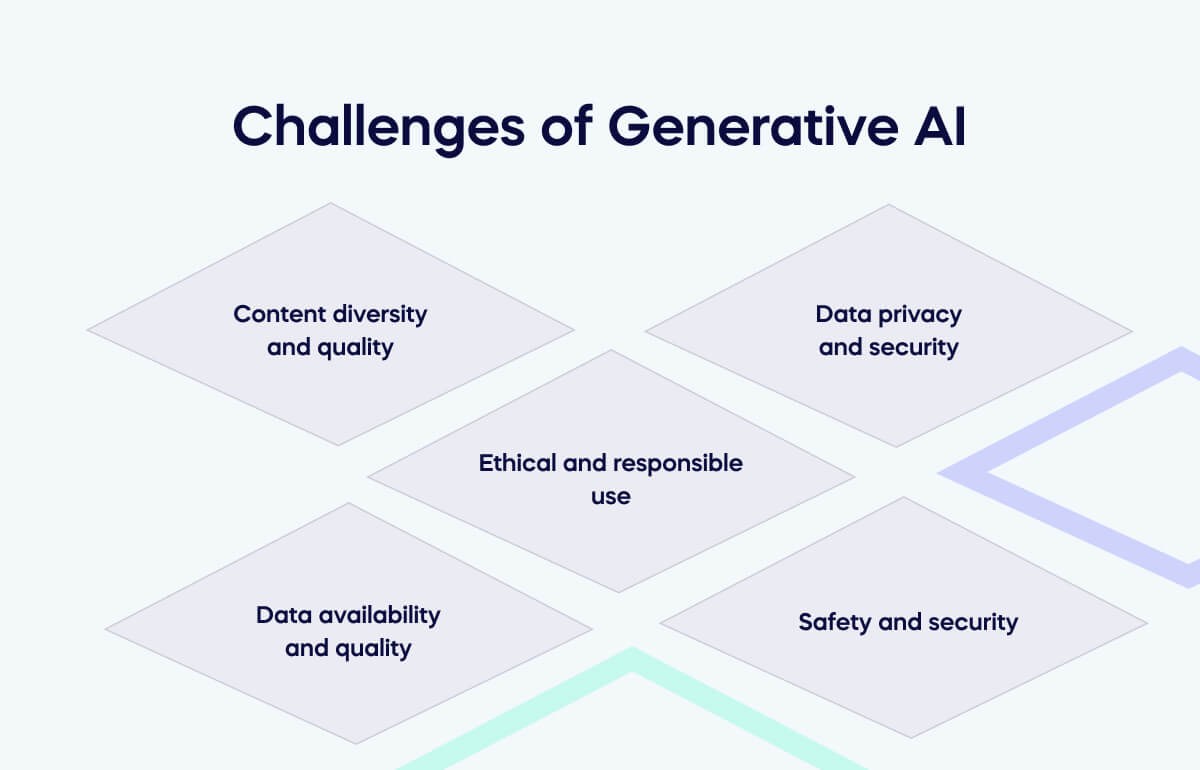
Another problem with generative AI is its reliance on pre-training. This means it is not always up to date, and you may not always have access to the latest information. Also, since it is generative, it can be wrong, so it is important not to trust blindly.
Finally, there is a risk of copyright infringement, as AI can generate content that infringes existing intellectual property.
However, the rise of AI is also a cause for concern. One such concern is the potential for toxic content. Because generative AI is trained on existing data, it can replicate or even amplify negative content.
AI can create convincing deep-fakes, which can lead to spoofing and other security issues. These deep-fakes, if not properly regulated, can damage people’s reputations and can cause serious harm. Imagine an AI-generated video with your actual face and attributes doing something illegal. That is how far this can go if not regulated.
Read Also: Embracing the magic power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in photography
Conclusion
Moving AI forward requires responsible governance and regulation. Large tech companies investing heavily in AI should prioritize AI governance and regulation to avoid unintended consequences. Regulation should address issues such as safety, copyright, and toxic content. In addition, companies should be transparent about how they create content using generative AI and its limitations.
Despite its challenges, AI also has many advantages. For example, it can be a co-pilot for many jobs, such as programmers, cooks, students, and anyone looking to improve their productivity. For instance, Chat GPT can rewrite emails in a calm and professional tone to prevent you from sending emails you regret
In addition, generative AI completes tasks faster, enabling companies to create more value by adopting AI. Microsoft has already added GPT to Teams, Bing, and other Office 365 suites, while tools like Lang Chain allow users to create and customize their own large language models to target specific domains and ideas.
Generative AI holds the potential to revolutionise many industries and make lives easier. However, like any technology, there are risks that need to be addressed. Responsible governance and regulation can maximize the potential of generative AI while minimizing its negative impacts.