- Abu Dhabi radiates optimism as over 300 startups join AIM Congress 2024
- TLcom Capital Raises $154 million in Funding to Boost Its African Growth
- Africa’s $824Bn debt, resource-backed opaque loans slowing growth — AfDB
- LB Investment brings $1.2 trillion portfolio display to AIM Congress spotlight
- AmCham Summit kicks off, setting course for robust future of US-East Africa trade ties
- Why the UN is raising the red flag on the UK-Rwanda asylum treaty
- Portugal’s Galp Energia projects 10 billion barrels in Namibia’s new oil find
- Wärtsilä Energy offers tips on how Africa can navigate energy transition and grid reliability
West Africa
Angola is also rich in other minerals like iron ores, diamonds, gold, marble and phosphate deposits. The embassy of Angola’s economic outlook indicates that from the 1950s through 1975, iron ores were explored in provinces such as Malange, Bié, Huambo, and Huíla, and average output reached 5.7 million tonnes per year between 1970 and 1974.
The most explored minerals were exported to Japan, Germany, and the United Kingdom, earning Angola US$50 million a year.
Angola’s phosphate deposits are estimated at 150 million tonnes, located in the provinces of Cabinda and Záire. These resources have so far been unexplored. In Southeastern Angola in the provinces of Namibe and Huíla, marble, granite, and quartz reserves abound. Marble is especially consumed in the local market, while black granite is on demand and exported to United States and Japanese markets.…
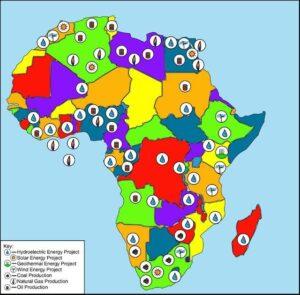
As Africa’s role in the global economy continues to garner prominence, it’s imperative for the continent to seal the gaping hole in its power supply.
Lack of universal power access remains a major roadblock that has retrogressed industrialization and socio-economic development. Statistics from the World Bank indicate that Africa remains the least electrified region in the world, with 568 million people lacking access to electricity.
The Bretton Woods institution, further notes that the Sub-Saharan Africa’s share of the global population without electricity, jumped to 77 per cent in 2020 from 71 per cent in 2018, whilst most regions saw declines in their share of access deficits. It has become a Hobson’s choice for African governments to prioritize the power sector, which is the epicenter of industrialization, working towards Goal 7 of the UN SDGs; which advocates for universal access to affordable, reliable and modern electricity services.
Currently, Africa’s power is …
The Nigerian Minister also praised Equatorial Guinea, saying that the Western African country has a massive record of world-class gas processing and liquefaction infrastructure already in Punta Europa and allocating investment funds for development.
Minister Obiang Lima said that Equatorial Guinea was in line to be an essential player in the African energy market.
“New, fast, and competitive sources will be a major determinant of success,” he said. “This strategic collaboration breaks down geographical boundaries and allows gas delivery from Nigeria to Equatorial Guinea’s Punta Europa facilities, extending their life and providing access to the regional and global energy markets.”
Through the agreement, the Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation (NNPC) and its joint venture partners will put into monetary use gas that would have otherwise been stranded offshore due to the absence of infrastructure.…
Three projects financed by the African Development Bank (AfDB) for US$121.4 million in 2010-2011 are starting to provide Cameroon with more reliable electricity supply, the bank said.
Although Cameroon has suffered power supply for years, it has the second-largest hydroelectric potential in Africa and the 18th worldwide with an estimated 23,000 MW hydroelectric production capacity.
In a statement given on Thursday, AfDB said the Lom Pangar storage reservoir project was complete, although the dam’s generating plant was still under construction. Two other power plants, Kribi and Dibamba, had begun working to strengthen the country’s generating capacity.
In November 2011, The African development bank awarded $62.9 million for the construction of Lom Pangar in the country’s eastern region and a 30 MW hydroelectric generating plant still under construction at the base of the dam. Lom Pangar will provide electricity to 150 locations and significantly reduce power cuts.
Also Read: Arabian and
…Zimbabwe expressed concern over the United States’ ban placed on its diamonds to prevent it from being imported over concerns of forced labour.
The US Customs and Border Protection banned targeted products from China, Zimbabwe and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). This has risen suspicion of the blockade being an extension of Washington DC’s trade war with China.
The US said that they issued a Withhold Release Order of the artisanal rough-cut diamonds from Zimbabwe’s Marange diamond field due to evidence of forced labour and the US law prohibits importation of goods made with forced labour.
The Secretary of Information, Publicity and Broadcasting Services Mr. Nick Mangwana responded, “There is virtually nothing like this in our diamond industry. Zimbabwe is replete with a highly qualified labour force which is neither forced nor compelled at any point along the mining and processing value chain.”
He pointed out that Zimbabwe …
Smile Train, the world’s leading cleft organization, announced their partnership with the West African College of Surgeons (WACS) to launch the Smile Train-WACS Cleft Surgical Certification. The Certification will grant 6 surgeons per year over the next five years the opportunity to specialize in cleft care across West Africa.
The one- year Post-Graduate Program will commence in February 2020. WACS will identify accredited centers to serve as training sites in Nigeria, Ghana and French West Africa. The Certification is open to applicants in all West African and CEMAC zone countries with priority being given to trainees from countries without significant Smile Train presence.
Smile Train empowers local medical professionals with training, funding, and resources to provide free cleft surgery and comprehensive cleft care to children globally.
Speaking during the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), Smile Train Program Director of West and Central Africa, Mrs. Nkeiruka Obi noted …
A report released at the African Green Revolution Forum in Accra finds that millions of small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) rarely are dependent on big multinationals for their raw materials but directly rely upon millions more smallholder farmers across Sub-Saharan Africa.
The report finds that, overall, only about 20 percent of the volume of food consumed in Africa fits the conventional notion of subsistence agriculture—food consumed directly by the farming households that grow it.
“All this represents a profound turnaround from mere decades ago, ” said Dr. Thomas Reardon of Michigan State University, a lead author of the report. “There has been a ‘Quiet Revolution’ in agrifood private sector value chains linking small farmers to burgeoning urban markets and growing towns in Africa. This has spurred farmers’ participation in food and farm input markets.”
SMEs provide a range of services, from transport and logistics to the sale of inputs such …
Global consultancy Palladium has announced its first impact investment fund to bridge the financing gap for small businesses in sub-Saharan Africa.
The “Palladium Impact Fund I” is expected to raise USD 40 million to provide much-needed capital for SMEs in emerging markets. The fund, which will focus on agribusiness value chains and off-grid clean energy in Nigeria, Ghana, and Kenya, aims to alleviate poverty and economically empower over 500,000 rural households. It intends to create at least 3,500 full-time jobs, of which 60 percent will be for women.
Investors will include foundations, family offices, pension funds, and institutional investors. Palladium will manage the fund, anchored by a $5 million investment of its own capital. The new fund will make debt and mezzanine investments of between $250,000 and $2 million into small companies.
Andrew Tillery, Head of Impact Investments at Palladium, said, “Fifty-four years of experience has taught Palladium that for …
PIDG company, the Emerging Africa Infrastructure Fund (EAIF) has announced that it has arranged the long-term debt finance for a €305 million new port development by Gabon Special Economic Zone Ports (GSEZ Ports) at Owendo, Gabon.
In addition to its sole mandated lead arranger role, EAIF is lending the company €40 million over 15 years, on a first ranked basis. GSEZ Ports is EAIF’s first project in Gabon. It is the largest industrial-scale infrastructure public-private partnership yet seen in the country. Financial close was achieved on 26 July.
The African Development Bank (AfDB), which led the structuring of the finance, is also lending €40 million. The new funds will refinance the project, releasing money for the largest shareholder to reinvest in other infrastructure projects in Africa, some in Gabon. 75% of the capital for the port project is shareholder equity.
GSEZ Ports has been awarded a 30-year concession to build …





![Sectors to revive Angola’s heavily indebted economy Oil-extraction-in-Angola. [Photo: Financial Fortune]](https://theexchange.africa/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/ANgola.jpg)