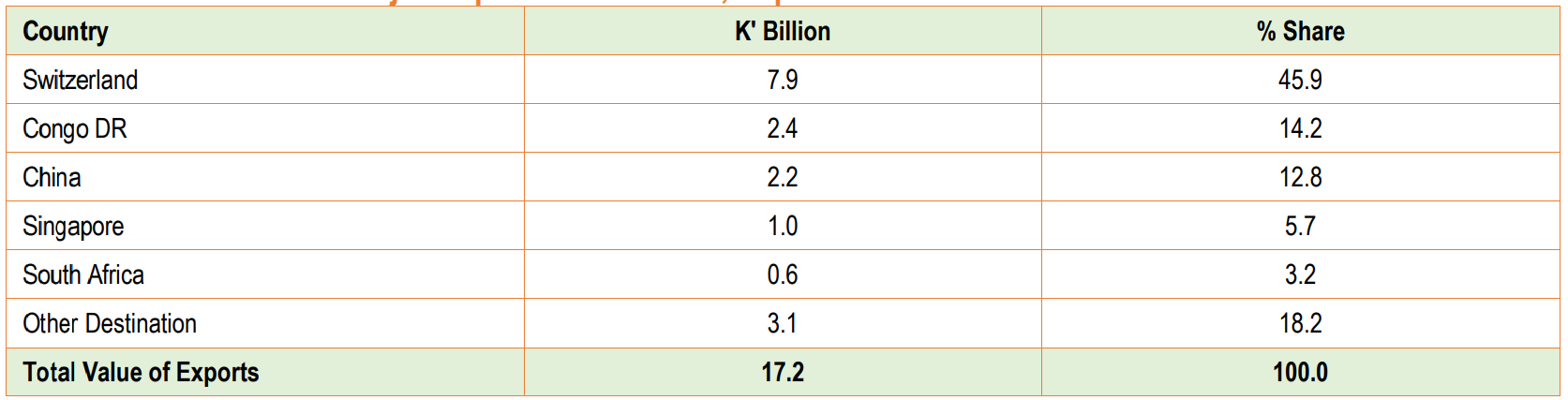
- The latest data from the Zambia Statistics Agency (ZAMSTATS) has placed Switzerland as the dominant force in Zambia’s export market.
- Zambia’s import sources and the primary imported goods provide a comprehensive view of the country’s international trade dynamics for September 2023.
- The total value of exports via all modes of transport for this period amounted to K155.6 billion.
The latest data from the Zambia Statistics Agency (ZAMSTATS) has placed Switzerland as the dominant force in Zambia’s export market. Switzerland accounted for a staggering 45.9 per cent of Zambia’s export earnings for September 2023.
ZAMSTATS’ October monthly bulletin reveals Switzerland’s dominant position as Zambia’s primary export destination. This is primarily driven by the export of copper anodes for electrolytic refining. Copper exports constitute a significant 73.4 per cent of total export earnings.
The Democratic Republic of Congo was the second-largest export destination for Zambia in September 2023. DRC accounted for 14.2 per cent of Zambia’s export earnings. Zambia’s primary exports to Congo DR included various kinds of sulphur. This makes up 12.8 per cent of the country’s export earnings.
Moreover, China, a vital trading partner, claimed the third position with 12.8 per cent of Zambia’s export earnings. Copper anodes for electrolytic refining were the main export product to China. They contributed to 59.8 per cent of export earnings from this market.
Singapore, in fourth place, accounted for 5.7 per cent of Zambia’s export earnings, primarily driven by the export of copper anodes for electrolytic refining, constituting 37.5 per cent of total export earnings from Singapore.
South Africa rounded up the top five export destinations, making up 3.2 per cent of Zambia’s export earnings in September 2023. The main export product was non-carded or combed cotton, which accounted for 16.8 per cent of export earnings.
Zambia’s international trade and non-traditional exports
Collectively, these five countries contributed to 81.8 per cent of Zambia’s export earnings in September 2023, emphasizing the critical role they play in Zambia’s international trade.
In addition to traditional exports, Zambia has also actively engaged in non-traditional exports (NTEs). In September 2023, the DRC remained the largest market for Zambia’s NTEs, accounting for 39.0 per cent of total NTE earnings. The primary export product to the DRC within the NTE category was sulfur, making up 12.8 per cent of total NTE earnings.
Read also: Understanding Zambia’s National Debt Crisis
Zambia’s export market shares by region
Furthermore, ZAMSTATS’ report delves into export market shares by selected regional groupings and significant trading partners. Switzerland’s dominance in the export market is especially evident, with the country accounting for a substantial 45.9 per cent of export earnings in September 2023.
Asia was the second-largest market, with a 20.8 per cent share of Zambia’s exports. Within this grouping, China stood out as the dominant market with 61.8 per cent of the claim, followed by Singapore with 27.3 per cent. Other regional sets included DUAL-SADC & COMESA (18.7 per cent), SADC Exclusive (9.4 per cent), COMESA Exclusive (1.6 per cent), and the European Union (1.5 per cent).
These statistics emphasize the significance of Switzerland as a key player in Zambia’s export market and highlight the country’s ongoing economic relationships with other important trading partners in the region.
Zambia’s key import sources and products in September 2023
In addition to its export destinations and products, Zambia’s import sources and the primary imported goods provide a comprehensive view of the country’s international trade dynamics for September 2023.
South Africa was the leading source of Zambia’s imports, accounting for 25.3 per cent of the import bill. The primary import products from South Africa included vehicles with diesel engines for transporting goods, particularly those with a Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) of up to 5 tonnes, contributing 3.9 per cent to the import bill.
China was the second primary source of imports, representing 14.5 per cent of Zambia’s import bill. The direct import product from China was road tractors for semi-trailers powered by diesel or semi-diesel engines, accounting for 12.8 per cent of the import bill.
The United Arab Emirates ranked third, making up 11.0 per cent of the import bill, with gas oils the significant import product, accounting for 32.4 per cent.
Japan, in fourth position, accounted for 6.2 per cent of the import bill, with dumpers designed for off-highway use being a significant import product, contributing 26.9 per cent to the import bill.
India was the fifth-largest import source, making up 5.5 per cent of the import bill, with first-aid boxes and kits accounting for 12.2 per cent.
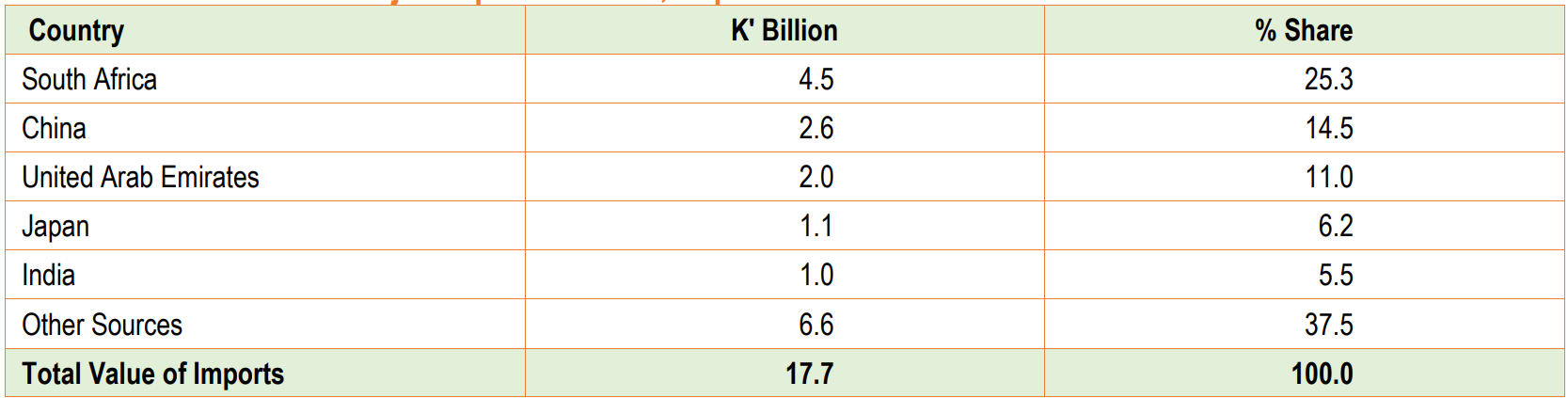
This data underscores the significant role these countries play in supplying Zambia with essential goods. Zambia needs to manage its import dependencies while exploring opportunities for domestic production and reducing trade imbalances.
Import market shares by regional groupings and trading partners
Furthermore, analyzing import market shares by selected regional groupings and significant trading partners, Asia emerged as the primary source of Zambia’s imports, constituting 51.5 per cent in September 2023, with China being the main contributor within this region. Other notable Asian markets included the United Arab Emirates, Japan, India, and Bahrain, collectively accounting for 53.0 per cent of imports from the continent.
SADC Exclusive came second in import market shares. The region contributed 32.4 per cent of Zambia’s import bill, with South Africa as the dominant source. Tanzania, Namibia, Mozambique, and Botswana also contributed to this grouping.
The EU accounted for 4.4 per cent of Zambia’s imports, with Germany as the primary source within this grouping. Belgium, Netherlands, Sweden, and Ireland collectively contributed significantly.
The Dual SADC & COMESA grouping contributed 4.1 per cent to the import bill in September 2023. Mauritius was the dominant source. Zimbabwe, Congo DR, Malawi, and Eswatini were also noteworthy contributors.
The COMESA exclusive grouping represented 0.8 per cent of the import bill, with Kenya as the leading market, followed by Uganda. Egypt, Tunisia, and Rwanda were also significant contributors to this grouping.
Exports by mode of transport in 2023
The total value of exports via all modes of transport for this period amounted to K155.6 billion. Among the various transportation modes, road transport played a dominant role. It accounted for the highest share at K74.1 billion, representing 47.6 per cent of total exports. Rail transport was the second most prominent mode, contributing K6.7 billion (4.3 per cent). Air transport came in third, accounting for K3.3 billion (2.1 per cent). Other modes of transport collectively accounted for K71.5 billion (45.9 per cent).
In terms of volume, 7.5 million metric tonnes (Mt) of exports were recorded during this period. Road transport carried the majority, with 4.1 million Mt, representing 53.7 per cent of the total volume. Rail transport handled 49.7 thousand Mt (0.7 per cent). Air transport contributed 2.5 thousand Mt (0.03 per cent). Other modes accounted for 3.4 million Mt (45.6 per cent).
Imports by modes of transport
Turning to imports, the total value of imports via all modes of transport for the same period reached K148.1 billion. Road transport emerged as the primary mode, responsible for K84.8 billion, representing a substantial 57.2 per cent share. Air transport was the second most significant, with K7.0 billion (4.8 per cent). Rail transport ranked third, contributing K2.5 billion (1.7 per cent). Other modes of transport covered K53.8 billion (36.3 per cent).
Regarding import volumes, 5.4 million Mt of goods entered Zambia from January to September 2023. Once again, road transport proved crucial, carrying 3.2 million Mt, accounting for a significant share of 58.9 per cent. Rail transport managed 211.0 thousand Mt (3.9 per cent). Air transport handled 6.8 thousand Mt (0.1 per cent). Other modes transported 2.0 million Mt (37.1 per cent).
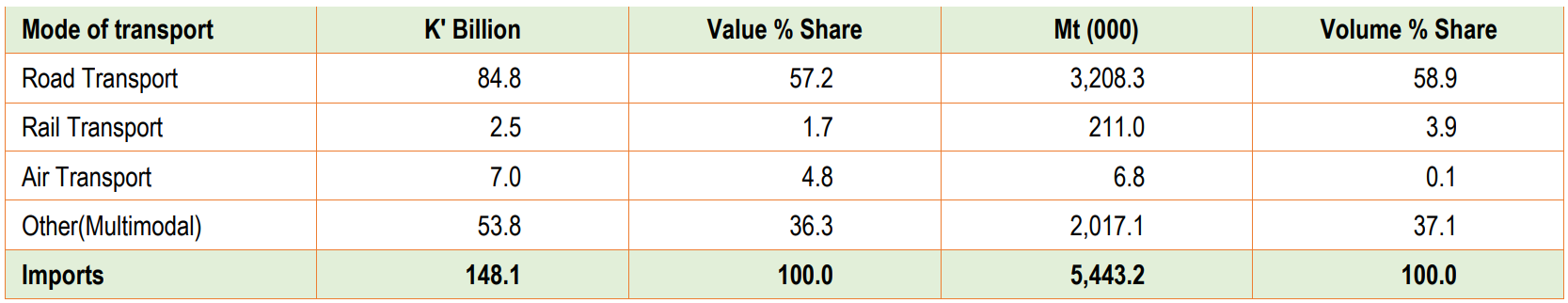
Consequently, this reveals the substantial impact of road transport on exports and imports. It highlights the importance of maintaining and enhancing road infrastructure to facilitate trade. Policymakers must consider these figures when planning the country’s transport and trade-related infrastructure developments.











