- Africa is an emerging market in forex trading, and its potential for growth is immense.
- Forex trading in Africa is a growing industry, but it faces significant challenges.
- These include lack of infrastructure, education, and awareness, coupled with fraudulent activities, have hindered its growth.
Online Forex trading in Africa is still in its nascent stage and is largely driven by the youth. In layman’s terms, forex trading is the act of buying and selling currencies to make profits based on speculating the relative upward or downward movements of currencies.
According to ForexSchoolOnline.com, the average age of forex traders is between 25-44 years old, with 9 per cent aged 65 or older. Only 37 per cent of traders are either breaking even or profitable, while 63 per cent are unprofitable. Most traders (72 per cent) have no experience trading other markets before forex, and 40 per cent of traders are attracted to forex trading because they want to be their own boss. Additionally, 70 per cent of traders, trade on a live account, and 39 per cent have traded for 1-3 years.
Further, the most popular trading platform is still the classic MT4, which is used by 85 per cent of traders. The second most popular platform is the MT5, which is used by only 6 per cent of traders.
What is the global forex market size?
According to BIS’s 2019 triennial survey, trading in forex markets reached an incredible US$6.6 trillion per day in April of 2019. The worth of the entire global forex trading market is estimated to be approximately US$2.4 quadrillion. In other words, around US$2409 trillion. Global GDP in 2019 amounted to roughly US$142 trillion. This means that the annual turnover of the forex market is almost 17 times larger than some of the largest securities exchange. The forex market dwarfs even the largest stock exchanges in the world – for example, Nasdaq has a daily volume that averages around $200 billion. Over 170 currencies are traded on the global forex market.
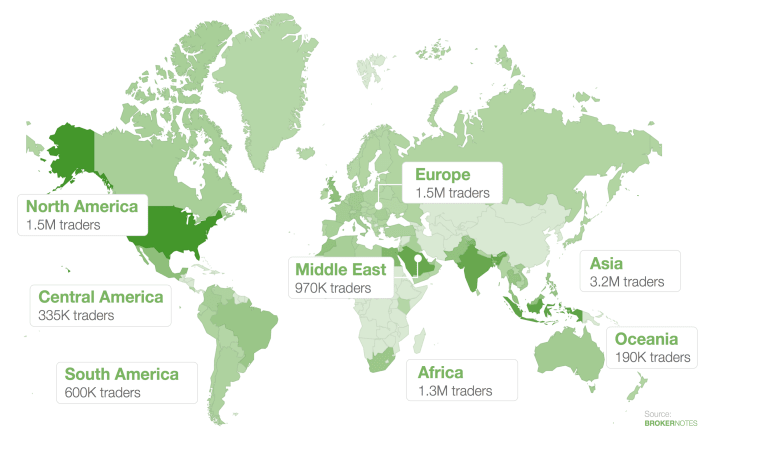
The forex market, however, in Africa is relatively small in comparison to the global market, with South Africa being the largest market in the region.
Read: The richest forex traders in South Africa
Is Forex trading legal in Africa?
Regulatory bodies play an important role in forex trading as they are responsible for ensuring that the market operates fairly and transparently. In Africa, regulatory bodies have been established in some countries to oversee forex trading activities. However, the regulatory environment in Africa is still in its early stages, and there are several challenges that regulatory bodies face.
Currently, some countries in Africa that have regulators supervising retail forex trading are Kenya, South Africa and Mauritius. But, retail forex trading in several countries is not regulated by governments.
Read: Forex trading in Kenya
According to an article by Nyasa Times, African countries without regulation are exposed to counterparty risk as there’s no local regulatory body that can take up the case for you in case broker goes bankrupt and fails in its obligations.
Further, due to absence of regulation of retail forex traders among many countries in Africa, there is no provision for compensation funds for Forex traders. Even in South Africa, where retail forex trading is regulated, the compensation schemes does not offer any compensation in case of misappropriation of funds by regulated brokers.
The regulatory body in charge of overseeing the Nigerian capital market went as far as to caution individuals who engage in forex trading that they bear full responsibility for any risks associated with it.
“The attention of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been drawn to the increased advertisements in electronic and other media soliciting investors to engage in leveraged online retail forex trading.
The public is hereby advised that online retail forex trading is currently unregulated and consequently may be subject to abuse,” read a statement on the regulator’s website.
South Africa has the most developed regulatory framework for forex trading in Africa. The Financial Services Conduct Authority (FSCA) is responsible for regulating forex trading activities in the country.
The challenges faced by regulatory bodies in Africa include limited resources and inadequate staffing. Regulatory bodies also face the challenge of keeping up with new technologies and innovations in the forex market
What are the problems faced by forex traders in Africa?
Forex trading in Africa is a growing industry, but it faces significant challenges. The lack of infrastructure, education, and awareness, coupled with fraudulent activities, have hindered its growth. The African continent is also diverse, and there is no single regulatory body overseeing forex trading. As a result, forex trading is mostly unregulated, making it more susceptible to fraudulent activities and scams.
One of the biggest challenges facing forex traders in Africa is the lack of infrastructure. Many countries in Africa have poor road networks, limited access to the internet, and inadequate power supply. This makes it difficult for forex traders to access the market, as they require reliable internet connectivity and access to trading platforms.
Additionally, there is a lack of education and awareness about forex trading in Africa. Many people are unaware of the potential for profit and the risks involved in forex trading. This lack of knowledge has led to fraudulent activities and scams, with many people falling victim to unscrupulous individuals promising unrealistic returns.
According to Nyasa Times, forex traders in Africa may also encounter difficulties when it comes to depositing and withdrawing funds in foreign currencies. This is because some forex brokers do not offer accounts in the local currency and some do not allow withdrawals to local bank accounts.
While international platforms such as PayPal may be available for fund withdrawals, not all African countries have access to these platforms. For example, countries like Cameroon, Libya, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Sudan, and Central African Republic are currently prohibited from using PayPal, making it challenging for Forex traders in those countries to conduct online transactions. Additionally, even if traders use other payment platforms like Skrill, they still need to convert the US dollar to the local currency, which may incur high fees.
Read: Forex Trading in South Africa, what you need to know