- Crowdfarming is a concept that aims to address these challenges by equipping smallholder farmers with the resources they need to grow crops and raise livestock.
- The global crowdfunding market was estimated to be over US$17 billion in 2020, with an annual growth rate of 16 per cent – 17 per cent.
- Between 2013 and 2016, over 78 per cent of annual African crowdfunding occurred in South Africa, Nigeria and Kenya.
When it comes to the agricultural sector in Africa, the concept of crowdfarming is shrouded in mystery. This relatively new phenomenon has attracted a lot of attention in recent years and is hailed by many as a solution to the many challenges faced by smallholder farmers on the continent. But what exactly is crowdfarming and what opportunities does it offer for investors and farmers alike?
First and foremost, it is important to understand the importance of agriculture in Africa. Despite the many obstacles faced by farmers on the continent, agriculture remains a vital sector that provides livelihoods for millions of people and contributes to the region’s overall economic growth.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO), agriculture contributes about 25 per cent of Africa’s gross domestic product (GDP) and employs more than 60 per cent of the continent’s labour force. This underscores the critical role agriculture plays in creating employment opportunities and fostering economic growth in the region.
In addition, the agricultural sector also makes an important contribution to Africa’s food security. The FAO reports that the continent has the potential to become a major food producer as it has vast areas of land suitable for agriculture and a favourable climate for growing crops. Despite this potential, however, the road to success for smallholder farmers in Africa is fraught with difficulties, including a lack of access to capital, technology and infrastructure.
Crowdfarming is a concept that aims to address these challenges by equipping smallholder farmers with the resources they need to grow crops and raise livestock. In this concept, a group of people collectively finance and support agricultural production by either investing in a farm or buying shares. The idea is that by pooling resources, smallholder farmers can get the support they need to succeed, while investors can reap the benefits of investing in agriculture.
Despite its potential, crowdfarming is not without its problems. This mysterious phenomenon has both advantages and disadvantages that need to be carefully weighed before investing. For example, one of the advantages of crowdfarming is improved access to capital for smallholder farmers, enabling them to acquire the equipment and inputs needed to grow crops and raise livestock. On the other hand, many African countries lack a legal framework for crowdfarming, which can expose investors to risks.
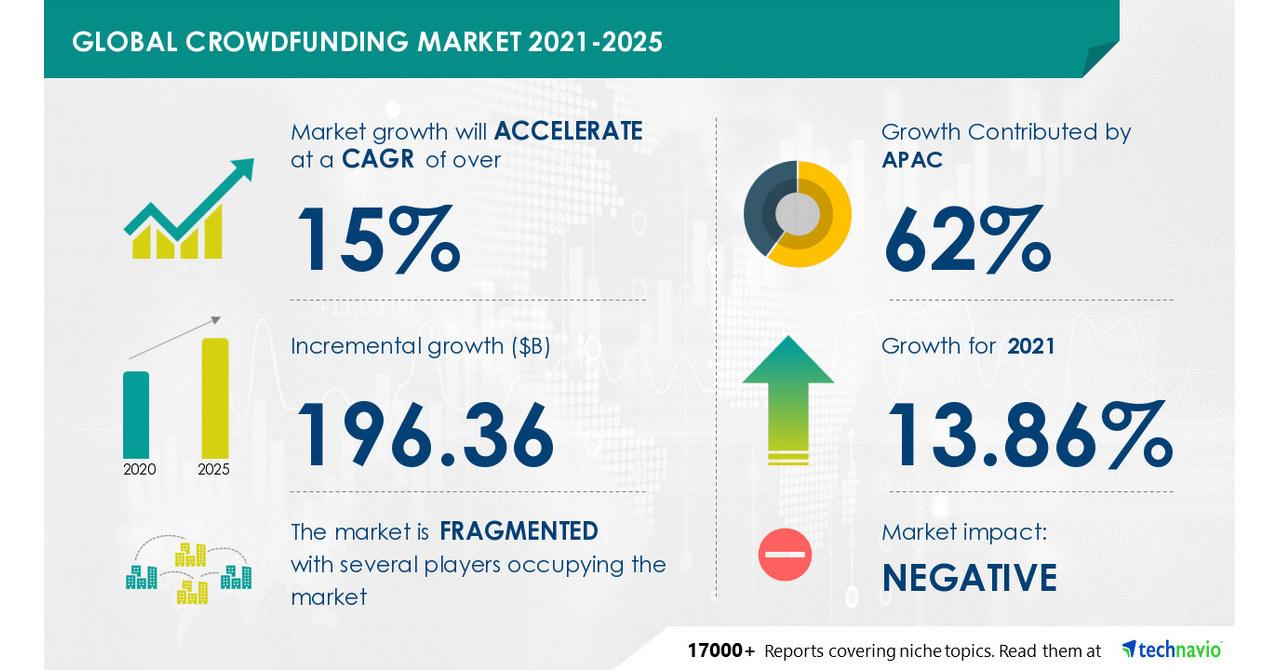
Equity crowdfunding in the US, Europe and the Orient continues to gain traction, but the concept is quite new in Africa.
Crowdfunding volumes in Africa have grown 118 per cent since 2015, with almost 90 per cent of capital being raised through foreign-based platforms headquartered in Europe and the United States. Between 2013 and 2016, over 78 per cent of annual African crowdfunding occurred in South Africa, Nigeria and Kenya.
So how can investors make money with crowdfarming?
Investors make money in crowdfarming through a variety of mechanisms, depending on the type of investment and the crowdfarming project in question.
One common way investors make money in crowdfarming is through a direct return on their investment, such as a share of the profit from the sale of the crops grown on the farm. In this model, investors can also receive a share in the land ownership or other assets associated with the farm.
Another way investors can make money in crowdfarming is through indirect returns, such as the increase in value of their investment over time. This is especially true in cases where the crowdfarming project involves the development of new, innovative technologies or methods for farming that can increase the value of the investment.
Finally, some investors choose crowdfarming to support the sustainable development of agriculture and food production in developing countries. While these investments may not yield large financial returns, they can provide a sense of social impact and personal satisfaction.
Setting up a crowdfarming initiative in Africa
Crowdfarming can be a powerful platform for individuals and organisations to support sustainable agriculture initiatives in Africa. Here is a step-by-step guide to setting up a crowdfarming initiative in Africa:
Develop a concept: Start by developing a clear concept for your crowdfarming initiative. This should include a detailed description of the farming project you want to support, the goals of the initiative and a description of the target group and market.
Identify a project: Next, identify a specific agricultural project in Africa that you would like to support with your crowdfarming initiative. This can be a small farm, a community farm, an organic farm or another type of agricultural project.
Do your due diligence: Before proceeding with your crowdfarming initiative, it is important to conduct due diligence on your chosen project. This should include a review of the project’s business plan, financial projections and any relevant market and industry trends.
Develop a crowdfunding campaign: Once you have completed your due diligence, it is time to develop a crowdfunding campaign for your project.
Launch the crowdfunding campaign: Launch your crowdfunding campaign and start promoting it to your target group. You can do this by reaching out to your personal network, promoting the campaign on social media and contacting relevant communities and organisations in Africa.
Manage the project: Once your crowdfarming initiative has been successfully funded, it is important to manage the project effectively. This includes regular communication with investors, progress reports and transparent reporting on the use of funds.
Measure success: Finally, measure the success of your crowdfarming initiative by tracking key metrics such as financial returns generated for investors, the impact of the project on the local community and the environment, and the level of engagement and support from investors and other stakeholders.
By following these steps, you can create a successful crowdfarming initiative in Africa that supports sustainable agricultural projects and generates financial returns for investors.