- Abu Dhabi radiates optimism as over 300 startups join AIM Congress 2024
- TLcom Capital Raises $154 million in Funding to Boost Its African Growth
- Africa’s $824Bn debt, resource-backed opaque loans slowing growth — AfDB
- LB Investment brings $1.2 trillion portfolio display to AIM Congress spotlight
- AmCham Summit kicks off, setting course for robust future of US-East Africa trade ties
- Why the UN is raising the red flag on the UK-Rwanda asylum treaty
- Portugal’s Galp Energia projects 10 billion barrels in Namibia’s new oil find
- Wärtsilä Energy offers tips on how Africa can navigate energy transition and grid reliability
Browsing: technology
Governments can play a crucial role in enhancing agricultural productivity in Africa for economic growth. Individual nations can accomplish this by establishing policy environments to promote agricultural investment, including providing tax incentives and subsidies to producers. Governments can also prioritize agricultural development in their national budgets by allocating a more significant proportion of their resources to the sector.…
An efficient crypto mining industry can generate more job opportunities in Africa as the demand for miners, blockchain specialists, and technology specialists increases, . This encourages nations to enhance their energy and technological capacities to support crypto operations. These enhancements can considerably benefit other industries and the economy as a whole.
African nations must embrace the chance to become a crypto mining hub. This can aid in the digital economy’s growth, citizens’ financial standing, and the infrastructure for energy production. Consequently, African governments can invest in cryptocurrencies to acquire alternative funding sources for developing renewable and alternative energy sources.…
- Digital technologies have enabled farmers to obtain crucial information on soil quality for nutrient levels, water levels, pests, and disease spread, captured from various sensors, satellites, and drones.
- One key area where technology can play a role in driving smart agriculture in Africa is through the use of chatbots.
- Chatbots have the potential to drive smart agriculture in Africa by improving crop yields, reducing costs, and increasing sustainability.
In Africa, where agriculture is a major contributor to the economy and a primary source of livelihood for many communities, the implementation of smart agriculture systems has a significant impact on food security and economic development. Smart agriculture refers to the use of advanced technology and data analysis to improve crop yields, reduce costs, and increase sustainability in the farming industry.
One key area where technology plays a role in driving smart agriculture in Africa is through the use of chatbots.
The …
- Liquid Cloud, Microsoft Collaborate to Deploy Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure in Africa
- Combining linear TV via satellite and on-demand services via OTT offers content in optimum quality at the convenience of the viewers.
Africa cannot afford to be complacent about digital transformation. The scale and complexity of Africa’s technical landscape sits at the heart of the problem, and connectivity issues are particularly prevalent.
Digital transformation offers Africa huge potential to overcome, even leapfrog, many of its perennial development and growth challenges.
The African telecommunication space has developed and has positively and significantly affected the growth of the economies on the continent in many ways. From enabling access to banking through mobile phones to interlinking the formal and informal economies that exist in the region.
Satellite combined with other technologies like fibre to form hybrid solutions is seen as critical to efforts by industry stakeholders to increase broadband connectivity in Africa especially …
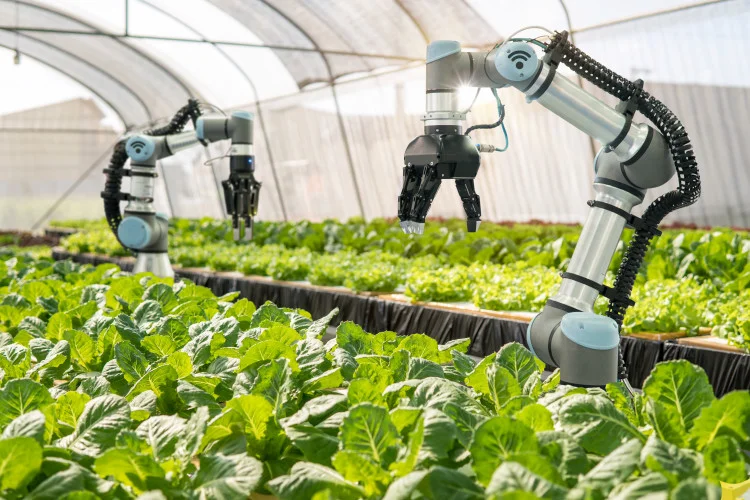
Integrating AI in farming machines will definitely help in optimizing operations. Investments in mechanization enable farmers to expand the range of their activities and diversify their livelihoods in ways that can reduce their vulnerability to climate change.
The availability of appropriate machinery to carry out sustainable crop management practices increases productivity per unit of land. It also increases efficiency in the various production and processing operations and in agricultural inputs’ production, extraction and transport. Artificial Intelligence methods support agriculture decision-making systems, help optimise storage and transport processes, and make it possible to predict the costs incurred depending on the chosen direction of management.
Tractor-operated tillage is the single most energy-consuming operation in crop production. Operating a plough is the main reason many farmers require high horsepower and diesel-fueled tractors. Conservation agriculture is flexible enough to accommodate the socio-economic resources of smallholder farmers as well as large-scale farming operations.…
The election of South Africa and other countries, on Monday, October 3, 2022, into different regional groups that constitute ITU Council was the highpoint of the Plenipotentiary Conference 2022 (PP-22) ongoing in Bucharest, the capital city of the Republic of Romania.
The seats in ITU Council are divided into five regions, A to E. South Africa was elected into the ITU Council Region D for Africa, which has 13 seats. The other 12 countries elected alongside South Africa are Algeria, Egypt, Ghana, Kenya, Mauritius, Morocco, Rwanda, Senegal, Nigeria, Tanzania, Tunisia, and Uganda.
Elections of member states also took place into Region A for The Americas (nine seats); Region B for Western Europe (eight seats); Region C for Eastern Europe & Northern Asia (five seats); and Region E, for Asia and Australasia with 13 seats as Africa.
The 21st Plenipotentiary Conference of the Council, also saw the election by member states, …
The world largely considers Africa as the next great growth market, a designation that has persisted for years. There are several reasons to be optimistic: the African continent has some of the world’s youngest populations, promises to be a key consuming market over the next three decades, and is becoming more mobile phone-enabled. Because access to smartphones and other devices improves consumer information, networking, job-creating resources, and even financial inclusion, a rising digital ecosystem is especially important as a multiplier of heightened economic growth.…
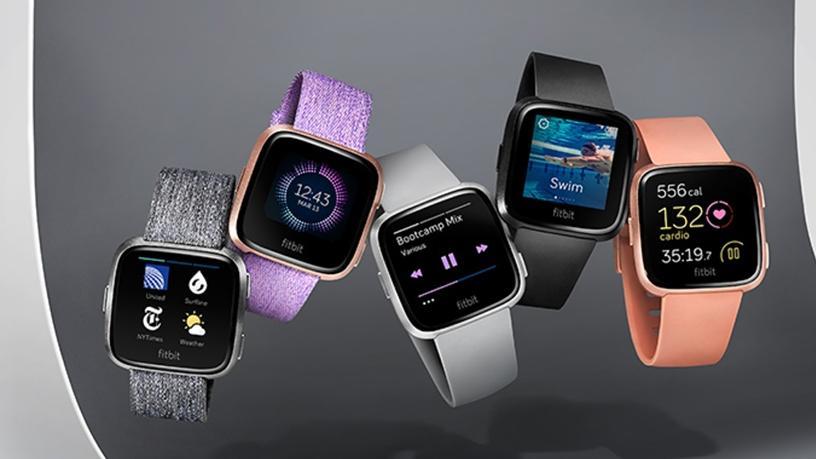
The market growth is extensively attributed to the rising health and fitness awareness, growing penetration of the internet & smartphones, and increased consumer disposable income levels.
The rising adoption has led to an increase in device development & innovation as more market players race in to deliver the growing demand and capture a higher market share.
According to Kewalramani, to set itself apart from competitors, Fitbit has evolved from being a pure fitness tracking device company to bringing more functionality and innovation around stress and sleep management to help users gain control of their health goals.…
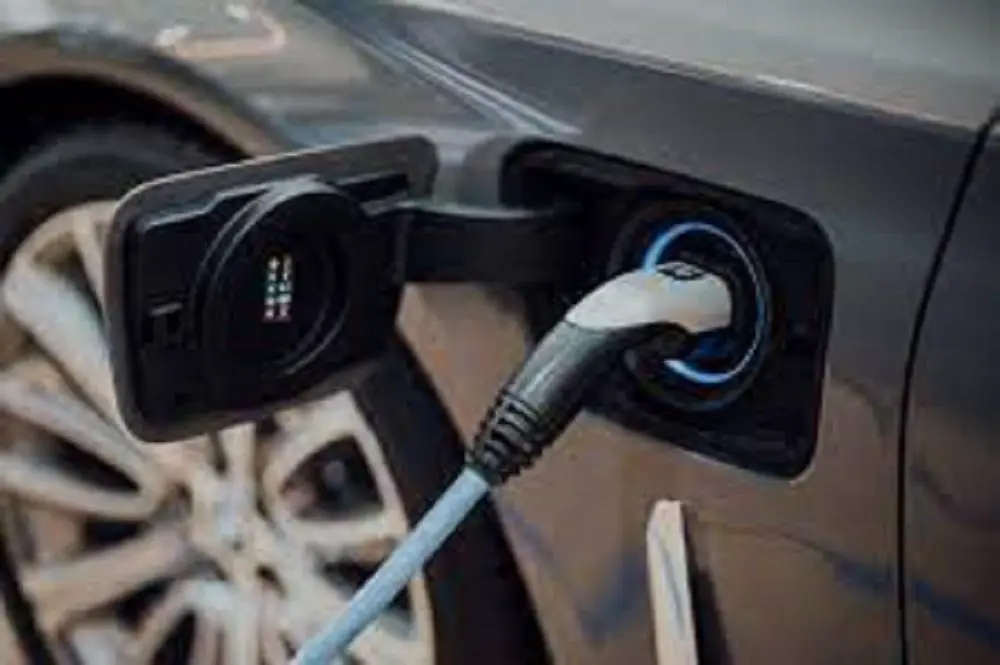
According to McKinsey published February 23, 2022, transport currently makes up 10 percent of Africa’s total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This is expected to increase in line with sub-Saharan Africa’s expanding vehicle parc.
South Africa, Kenya, Rwanda, Uganda, Ethiopia, and Nigeria make up around 70 per cent of Africa’s annual vehicle sales and 45 per cent of the region’s population.
The vehicle parc is expected to grow from 25 million vehicles today to an estimated 58 million by 2040, driven by urbanization and rising incomes. As its vehicle parc grows, the challenge for Africa will be to push for more sustainable mobility and avoid the risk of becoming the dumping ground for the world’s unwanted used ICE vehicles.…
IPv4 was the first version of IP to be used, and despite having been officially released in 1983, it is still the most widely used version to identify devices on a given network.
According to the CA report, with the imminent exhaustion of IPv4 address space, the length of IP addresses was increased from 32 bits to 128 bits, creating almost 340 undecillion addresses. The two address sets are not compatible, implying data sent using IPv4 address cannot be delivered to a recipient using IPv6 addresses.
The IPv6 was developed and standardized, as the next-generation Internet Protocol in 1996, with initial assignments for use in 1999, had the main goal of massively increasing the number of IP addresses available. Over the past year, major content providers and access networks have started offering IPv6 services to ordinary Internet users.…