- Kenyan Farmers Receive $2M Boost from Africa Fertiliser Financing Mechanism
- Brace for High Interest Rates for a Longer Period World Bank Warns Kenya
- Kenya-Ethiopia Trade Relations: Legislators Advocate for Policy Alignment to Boost Ties
- Visualising the state of debt in Africa 2024
- Abu Dhabi radiates optimism as over 300 startups join AIM Congress 2024
- TLcom Capital Raises $154 million in Funding to Boost Its African Growth
- Africa’s $824Bn debt, resource-backed opaque loans slowing growth — AfDB
- LB Investment brings $1.2 trillion portfolio display to AIM Congress spotlight
Regional Markets
- East Africa’s economic growth is projected to grow at 5.3 and 5.8 per cent in 2024 and 2025-26, respectively.
- The World Bank projects African economies to grow by 3.4 per cent in 2024.
- However, faster and more equitable growth is needed to reduce poverty.
East Africa’s economic growth to lead the continent
Economies in East Africa are expected to spearhead growth in Sub-Saharan Africa this year amid increased private consumption and declining inflation, which are supporting an economic rebound in the region.
The World Bank’s latest Africa’s Pulse report indicates the East African Community is projected to grow at the fastest pace at 5.3 and 5.8 per cent in 2024 and 2025–2026, respectively, thanks to robust growth in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Kenya, Rwanda, and Uganda.
This is higher than the compounded growth for Sub-Sahara Africa, which, albeit rebounding from a low of 2.6 per cent in 2023, is …
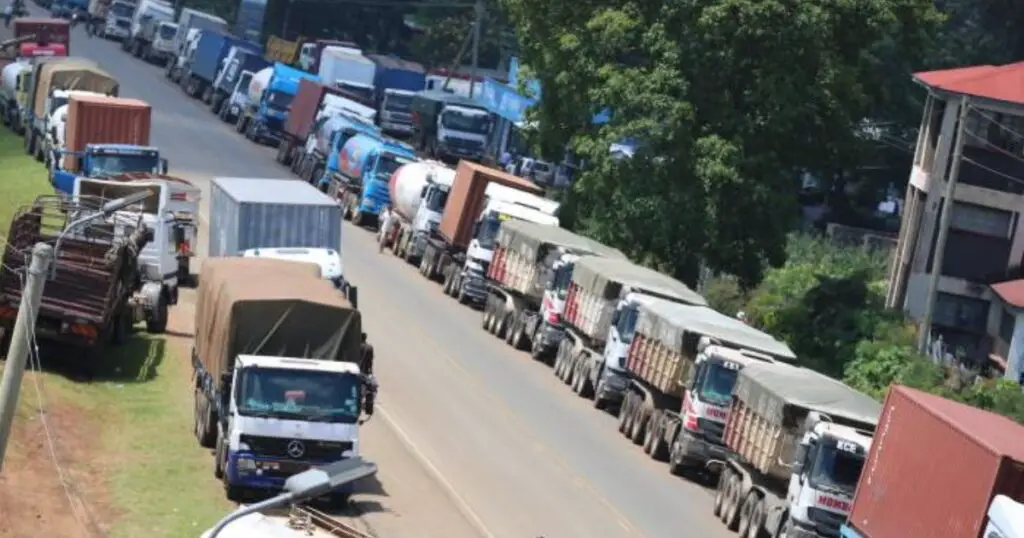
- Kenya is keen on extending its pipeline to Malaba (Kenya-Uganda border), with Uganda expected to construct a link line to Kampala.
- According to the Shippers Council of Eastern Africa (SCEA), Mombasa used to command up to 70% of transit business, but this has decreased to 60 per cent.
- Uganda imports an average of 2.5 billion litres of petroleum annually, valued at about $2 billion, with KPC handling at least 90 per cent of the volumes.
Kenya is courting Uganda in a fresh bid to retain and possibly increase petroleum exports amid increased competition from neighbouring Tanzania. In recent months, East Africa’s economic powerhouse has come under pressure from Tanzania, which is eyeing to tap more transit markets for imports and exports into the hinterland through the Dar es Salaam Port.
In the latest developments, Tanzania has offered to license Uganda National Oil Company (UNOC) to import petroleum products through Dar …
- Kenya’s equity market has received an upgrade on its classification by the FTSE Russel Index from “Restricted’ to “Pass” on the repatriation of capital and income.
- This development partly indicates that Kenya is now a maturing market, characterised by increased transparency, liquidity, and a growing investor confidence.
- Across Africa, data shows that an estimated $700 million was reported held in 11 African countries, with Nigeria accounting for the lion’s share.
FTSE Russell, a global provider of analytics, benchmarks and data services, has endorsed the Nairobi Securities Exchange Plc (NSE), ushering a new era in Kenya’s financial services industry. The NSE has announced that as of March 2024, the Nairobi bourse has been reclassified by the FTSE Russell Governance Board, moving from a “restricted” to a “pass” status.
This pivotal change is not just a mark of progress, but a move to underscore the resilience and strategic navigation of the Kenyan …
Most of the countries have no choice but borrow to bridge budget deficits. According to the IMF, the major EAC nations, namely Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Burundi and Rwanda, together, had borrowed more than $100 billion in both external and domestic borrowing.
With the global economy in teeters post Covid-19 and the impact of the Ukraine-Russia conflict, economies worldwide are contracting, leaving East African nations in a perilous situation.
According to the IMF, about
- Kenya’s Athi River Mining Cement PLC administrators have called for a creditors meeting to discuss liquidator’s acts and dealings.
- The Company was placed under Administration effective 17 August 2018 and subsequently placed in liquidation effective 1 October 2021.
- Creditors entitled to attend the meeting are entitled to appoint a proxy to attend and ask questions on their behalf.
Kenya’s Athi River Mining Cement PLC administrators have called for a creditors meeting to discuss liquidator’s acts and dealings, and the conduct of the liquidation during the preceding year.
The Company was placed under Administration effective 17 August 2018 and subsequently placed in liquidation effective 1 October 2021.
“Section 413 (1) of the Act provides that, if the liquidation of the Company continues for a period of twelve months or more, the Liquidator shall convene a meeting of the Creditors. In line with the above, notice is therefore hereby given that a …
- Britam Holdings Board of Directors has appointed Lofti Baccouche of Capgemini Invent in the UK as an Independent Non- executive Director.
- The appointment is subject to the Insurance Regulatory Authority’s approval amidst a low insurance penetration in the country.
- Lotfi is a financial services executive with solid experience in both developed and emerging markets with over 35 years of experience in finance, insurance and risk management.
Britam Holdings Board of Directors has appointed United Kingdom’s Lofti Baccouche the Vice President – Insurance practice lead in Capgemini Invent in the UK as an Independent Non- executive Director.
The appointment is subject to the Insurance Regulatory Authority’s approval amidst a low insurance penetration in the country.
Lotfi is a financial services executive with solid experience in both developed and emerging markets with over 35 years of experience in finance, insurance and risk management. He has wide experience in multiple countries across Africa, …
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) boasts of some of Africa’s largest economies, but like many economies of the world, the 15 member states of ECOWAS are facing both endemic and global challenges that could undermine the region’s economic growth in in 2023.
While two years ago in 2020, before the global pandemic struck, a majority of ECOWAS countries were enjoying the commodity boom with the region’s three of its largest economies – Nigeria, Ghana, and Côte d’Ivoire – accounting for one-fourth of Africa’s GDP.
Unfortunately, short of a change in the global economic projection, it will be a challenge for these West African countries to replicate the pre-pandemic growth. The global economic forecast paints a depressed economy in2023 and at best sluggish growth for more diversified economies, spilling over from the after math of the pandemic, the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and widespread inflation.
A global analysis released …
Africa is huge continent with untapped potential. With the rest of the world opening up for the best international trade and travel relations, Africa is learning and following the same path, with countries such as Uganda, Kenya and Rwanda easing entry restrictions by issuing visa on arrival and hence turning themselves towards open borders opportunities as members of the East African Community (EAC).
Unrestricted movement of people and goods between African countries holds the key to unlocking this trade potential. That is why trade analysts are touting the African Continent Free Trade Area (AfCTA) as a game changer in inter-Africa trade.
According to United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), Intra-African trade is currently low at 14.4 percent of total African exports. UNCTAD estimates that the AfCFTA could boost intra-African trade by about 33 percent and cut the continent’s trade deficit by 51 percent.
The possibility of more open …
But what is expected of