- Exports expanded from N$400 in 2020 to N$1.4 billion in 2022.
- The fact that Namibia is able to export to countries in Europe highlights the potential for Africa to expand its trade relationships with other regions of the world.
- This diversification is important for SADC region countries since it reduces reliance on a single commodity.
Namibia’s fruits and nuts industry has seen significant growth in recent years, with exports worth over N$1.4 billion between November 2021 and November 2022. This is a significant figure compared to imports, which were just shy of N$400 million. This export bill, although dominated by grape exports, shows that Namibia has a good market in Europe, especially in the United Kingdom, Germany, and The Netherlands.
Grapes and dates are considered the gold of the southern part of the country. However, there have been claims that producers are exploiting labor. Workers have constantly complained of late payment of salaries, while some sleep in makeshift houses made of boxes and other substandard materials.
Data from the Namibia Statistics Agency, which was released for November, shows that N$371 million worth of fruits and nuts were exported, mostly to The Netherlands. The agriculture ministry spokesperson, Jona Musheko, said the Namibian billion-dollar mark is a good sign that the fruits and vegetables subsector is growing and changing the status quo of Namibia as being a net importer.
“It is our wish that this begins to show in other subsectors such as grains,” he said. However, grain imports remain high, and maize imports for the month were recorded at N$42 million.
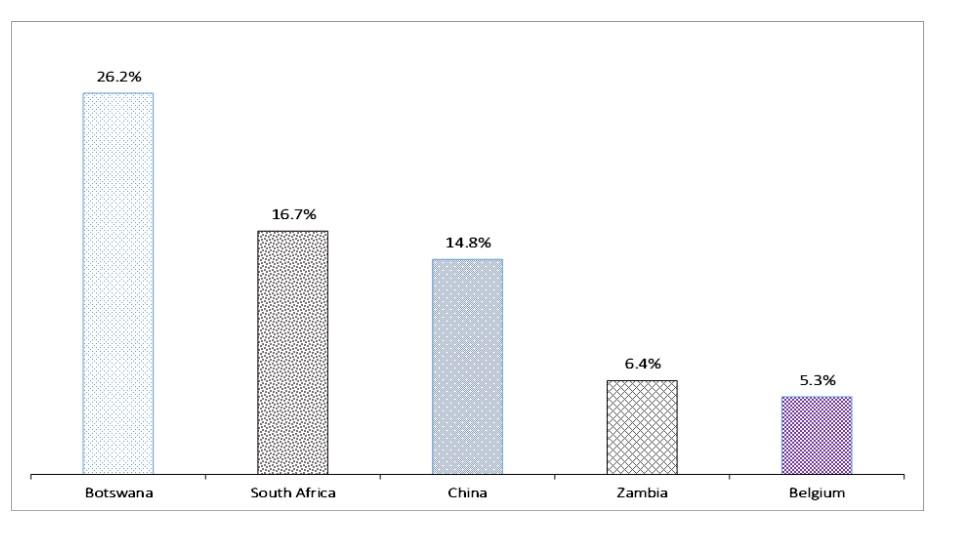
Furthermore, China, Zambia, and Belgium formed part of Namibia’s top five export markets. On the demand side, South Africa maintained her first position as the country’s largest source of imports, accounting for 45.6 per cent of total imports into Namibia, followed by China in the second position with 9.2 per cent of the market share. India, Italy, and the United States also formed part of Namibia’s top five import markets.
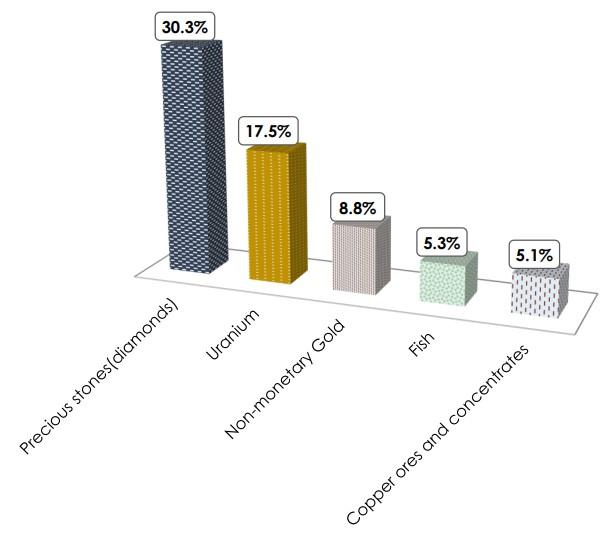
In terms of imports, petroleum oils were the highest valued commodity with a share of 14.6 per cent of total imports, followed by motor vehicles for the transportation of goods (4.1 per cent) and miscellaneous chemical products third at 3 per cent. Furthermore, alcoholic beverages accounted for 2.3 per cent, while telecommunications equipment contributed 2.2 per cent to Namibia’s total imports.
Read: Namibia: Mines Ministry extends Rössing’s Uranium mining licence for another decade
Namibia’s trade by mode of transport revealed that in November 2022, most goods were exported via air, accounting for 39.9 per cent of total exports. From the demand side, road transport was the most frequent mode of transport, accounting for 58.6 per cent of total imports.
The growth of Namibia’s fruits and nuts industry and its exports to countries in Europe and the SADC region (Southern Africa Development Community) can be seen as a sign of the country’s increasing importance in the regional economy. The fact that Botswana is the largest export destination and South Africa is the largest source of imports, highlights the strong trade relationships that Namibia has within the SADC region.
The fact that Namibia is exporting a significant amount of fruits and nuts, which is a sector that has traditionally been a net importer, is a positive indication of the country’s economic diversification and development. This diversification is important for SADC region countries since it reduces reliance on a single commodity and makes the economy less vulnerable to fluctuations in global commodity prices.
The growth of Namibia’s fruits and nuts industry and its exports to countries in Europe and the SADC region can be seen as a positive indication of Africa’s potential for economic development and diversification. The growth of this sub-sector shows that the country is capable of developing and expanding its agricultural industry. This is important for Africa as a whole, as agriculture is a major sector of many African economies and has the potential to drive economic growth and development.
Additionally, the fact that Namibia is able to export to countries in Europe highlights the potential for Africa to expand its trade relationships with other regions of the world. This can help to create more economic opportunities and contribute to reducing poverty and improving the standard of living on the continent.
This also potrays that Africa is becoming more self-sufficient and can provide for itself, this will in turn boost their economy and reduce the dependency on import which is important for their trade balance. However, it’s important to note that this is just one example of a country in Africa, and the economic situation in other countries on the continent may be different.
With the growth of this industry, it is important for the government to continue to support and invest in the sector to ensure its continued success. The government also needs to address the challenges faced by workers in the industry, such as late payment of salaries and substandard living conditions. As Namibia continues to diversify its exports and strengthen its trade relationships, the fruits and nuts industry has the potential to play an even bigger role in the country’s economy.











