- Rwanda and Kenya lead E. Africa in the list of most entrepreneurial countries in Africa.
- All other five East African countries do not make Africa’s top 10 list.
- Fintech remains the leader in entrepreneurship growth in Africa.
Entrepreneurship is growing at a tremendous rate across Africa and is to date the most powerful catalyst for economic growth and creation of employment for youth.
According to the UN Assistant Secretary-General and Director of the UN Development Program Ahunna Eziakonwa, digital innovation is the leading enterprise in Africa.
Entrepreneurship, a solution to poverty
The diplomat also recognizes the diversity that Africa’s vastness offers numeurous opportunities but on the other hand creates new challenges to ‘creating universal solutions for issues such as poverty and food security, because each country has its own capacity for innovation.’
“I think one of the flaws in development practice in the past has been taking Africa almost as a country and [applying] the blueprint development template,” Eziakonwa says.
“It’s very diverse – it’s 54 different countries at different stages of their development and with different contexts and dynamics. And it’s important, therefore, that any investment first tries to understand this diversity and the specific context of each country, but also the capacities and capabilities in each place, and then target your interventions based on that reality on the ground.”
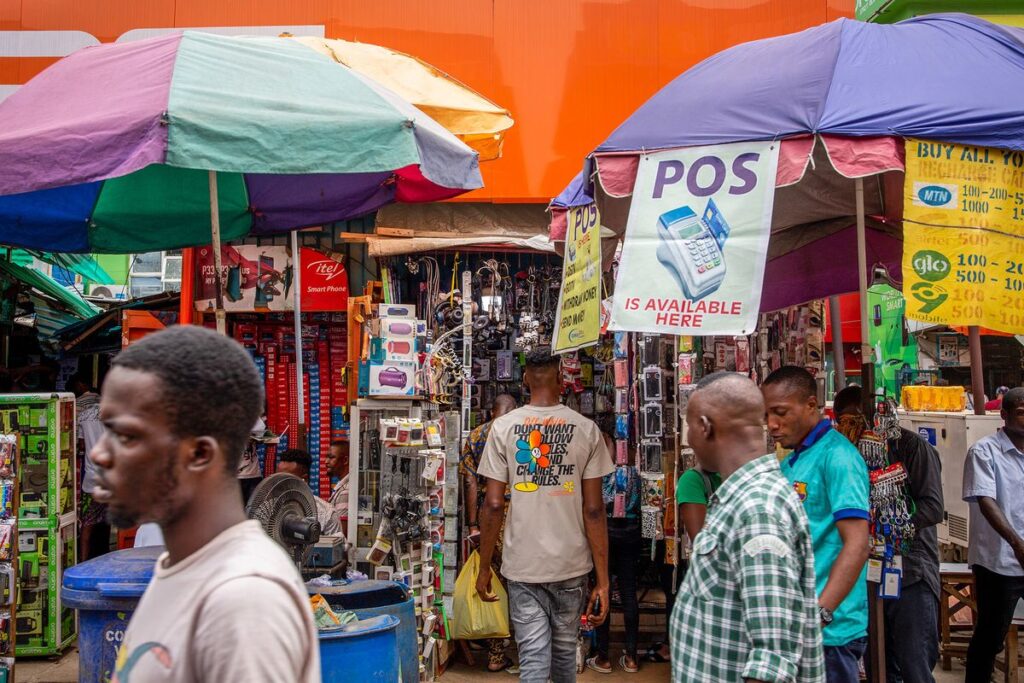
Nonetheless, while the diplomat acknowledges that most forms of self employment jobs in Africa involve the selling and reselling of crops and various goods; he, however, points out that there has been an extremely lucrative growth of business start-ups in the fintech industry.
Global payment options
It The global journey of the fintech industry took a decisive stance in 1998 when PayPal was established. It was one of the very first modern global payment options that allowed the transfer of cash digitally in normal day-to-day transactions.
By the end of 2022, there were well over 26,000 FinTech companies globally. Furthermore, not only does the industry represent the fastest growth in African entrepreneurship, it also represents the most lucrative enterprises. Case and point; Over 300 of the 26 000 FinTech companies are each worth over $1 billion.
Whether you’re moving money between accounts on your banking app, sending money to friends to split the dinner bill, trading stocks online, or paying for your coffee with a tap on your phone, all of this and more falls under the fintech -or financial technologies- umbrella.
The growth of fintech and its global adoption has been steadily gaining over the years, and there have been many drivers. A significant turning point was the 2008 global financial crisis, which dramatically shifted consumer trust, perception, and behavior, and increased demand for alternatives to the traditional financial banking system, fueling fintech innovations, including blockchain technology and digital currencies.
Read also: Dubai-Africa partnership, a new era of growth & prosperity with HE Hamad Buamim
Highest-earning enterprises
It was 1998 when PayPal was established as one of the first modern-day global payments companies. As of the end of 2022, there were well over 26,000 FinTech companies globally. Not only did the fintech industry grow in number of companies but it also represents some of the highest earning enterprises.
Notably, of the mentioned twenty thousand plus companies, more than 300 of them are worth over $1 billion, each.
To give you a glimpse of what fintech encompasses, it covers from major transactions like moving money between bank accounts using mobile banking apps all the way to simply sending a friend some money to split the dinner bill.
Fintech companies again range from trading stocks online to making a mobile payment for the smallest of purchases, say a cup of coffee. They cover blockchain technology digital currencies and any form of mobile money transfer; all these small and major transactions fall under the financial technologies umbrella that is now commonly known as the fintech industry.
For the developed World, the growth of fintech and its adoption found its turning point in the 2008 global financial crisis. At that point, there was a significant shift in consumer trust and behavior in traditional banking and investment options.
Simply put, people wanted alternatives to the traditional financial banking system, and guess who was there to offer the solution? The fintech industry.
Fintech driving financial inclusion
In Africa, the development of the Fintech industry has brought huge financial inclusion for the otherwise unbanked communities of remote areas in the country.
Previously, it was simply not feasible to set up bank branches in rural Africa but with the penetration of mobile phones and internet to these remote areas, the fintech industry covered the gap.
Now, across Africa, you can send and receive money from the remotest of areas anywhere on the continent. Africa’s fintech industry represents a total transaction value of $994 as of 2023.
This value is set to exceed $65 billion by 2030, this according to the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) enjoying and annual growth rate of 13 percent.
Also Read: Entrepreneurship, free trade Africa’s pandemic recovery ticket
Generally speaking, fintech or not, entrepreneurship is growing in Africa. As a new report by the CEO World magazine has shown. It assessed over 100 economies touching all vital measuring aspects including innovation, competitiveness, infrastructure, labour skills, access to capital, and openness for business.
The research results listed ‘the top 10 most entrepreneurial countries in Africa’ known as the Entrepreneurship Index.
Top 10 most entrepreneurial countries in Africa
- South Africa: South Africa takes the lead as the most entrepreneurial country in Africa. South Africa boasts the second-largest economy on the continent and is a hub for industrialisation. It has highly-skilled workforce, competitive spirit, and a business-friendly environment.
- Rwanda: At second place, Rwanda’s dedication to innovation, coupled with improvements in infrastructure and business openness, has spurred a thriving startup culture.
- Morocco: Morocco secures the third spot. The north African country has a growing pool of skilled labour. Coupled with increasing competitiveness and access to capital, Morocco fosters favourable environment for startups to flourish.
- Kenya: At number four, Kenya is a hotbed for entrepreneurial endeavours. The nation’s resilience, growing innovation landscape and positive infrastructure developments fuel its entrepreneurial spirit.
- Nigeria: Securing the fifth position, Nigeria remains a powerhouse for entrepreneurship in Africa. Nigeria’s startup scene benefits from improving access to capital and an open business environment.
- Tunisia: Tunisia embraces innovation and competitiveness, placing it in the sixth spot. The country’s efforts to support small businesses and enhance infrastructure contribute to its thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Ghana: Ghana’s commitment to nurturing startups has landed it in the seventh position. The country’s favourable labour skills and openness for business have provided fertile ground for entrepreneurs to thrive.
- Botswana: In eighth place, Botswana showcases its dedication to fostering entrepreneurship. A growing economy, improved infrastructure, and a supportive business environment have contributed to its success.
- Cameroon: Cameroon embraces a burgeoning entrepreneurial spirit, ranking ninth. The country’s efforts to improve access to capital and enhance business openness have been instrumental in supporting startups.
- Egypt: Completing the top 10, Egypt is driving entrepreneurship with its vast potential and growing innovation culture. The country’s diverse labour skills and efforts to promote business openness have laid a solid foundation for startups.
List Source – CEO World magazine