- Africa’s new dawn: the rising role of digital and AI in agriculture
- Can Dangote Refinery Transform Africa Energy Ambition
- Gallup Survey: 80 per cent of Kenyan Workers Are Disengaged and Seek New Opportunities
- Madagascar Man Freed from 5KG Tumor After 15-Year Struggle
- How women in Africa are perceived and treated
- Sugar consumption in Kenya to Increase to 1.23 Million Tonnes
- Can Somalia and Turkey Oil deal Bring Change in Somaliland
- Remittances to Kenya dropped to $371.6 million in June, marking a six month low
Browsing: Climate change
However, the DW report argued that just 18 per cent of GCF financing went to projects in the world’s poorest countries, while 65 per cent went to projects in middle-income countries like Mexico or India.
GCF is an essential partner towards Africa’s climate action. It is one of the most potent multilateral financing mechanisms available for the continent in supporting genuine-time climate action efforts.
Despite the underlying challenges within climate finance the region faces, it ought to be ready to harness GCF’s potential and become resilient as climate change impacts do not wait. …
Because outside of the governments, politicians, civil servants, lobbyists and pressure groups that thronged the Conference there is a cohort of entrepreneurs that are passionate about reversing climate change, that have fantastic commercially viable and innovative ideas, but who require funding and strategic support to make these ideas a reality.
And so I want to suggest that as well as taking personal responsibility for our carbon footprint and doing all that we can to minimise our negative impact on Planet Earth, we should also be investing in line with environmental, social and governance principles at all times – and ensuring that 20% of our investments in 2021/22 should be directly targeted at investments that will have a positive environmental impact. …
- US, EU pledge to cut global methane and greenhouse gas emissions by at least 30 per cent by 2030.
- 16 Southern African Development Community (SADC) states have recorded 36 per cent of all weather-related disasters in Africa.
- China, the world’s largest emitter of methane, India and Russia are not part of a pledge to cut down emissions.
The 26th Conference of Parties (COP26) has demonstrated to the world action towards climate change is possible.
As heads of state converge and pledge crucial issues including, the US and European Union announced a global methane pledge, cutting emissions of greenhouse gas by at least 30 per cent by 2030.
The conference, which is attended by countries that signed the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), has been drawing international attention as climate change impacts the global economy, especially developing economies across the world.
In that context, Africa as a region …
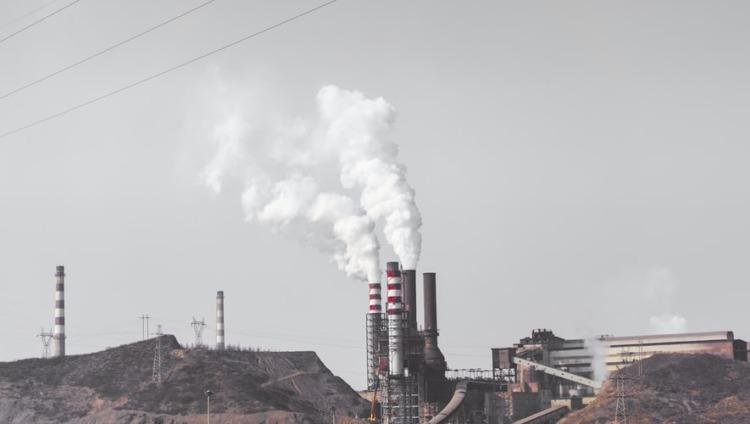
The pursuit of a greener earth and universal reliance on renewable presents a unique dilemma for countries in Sub Saharan Africa which rely heavily on energy provided by coal, shale, and other fossil fuels but also their economic livelihoods depend on the black gold.
The elimination of coal and related energy sources would severely prejudice economies that constitute SSA which are still developing or emerging.
It is against this background that the outgoing Chief Executive of the largest coal miner on the JSE, who is also the President of the Minerals Council is on record for saying that African countries should be allowed to make the transition from fossil fuels to greener renewable energies at their own pace. …
China had been funding the development and exploitation of massive coal reserves in countries like Indonesia and Vietnam under an initiative called the Belt & Road but has come under pressure as the world tries to honour its Paris climate agreements.
This Belt & Road initiative is a strategy initiated by the People’s Republic of China that seeks to connect Asia with Africa and Europe via land and maritime networks with the aim of improving regional integration, increasing trade and stimulating economic growth.
To realize this vision required the use of natural resources which China does not have entirely but other nations do and would then secure supply of this through the development of resources such as coal mines in developing countries. The Chinese are reportedly developing a US$3 billion coal mine in the Hwange area of Zimbabwe.…
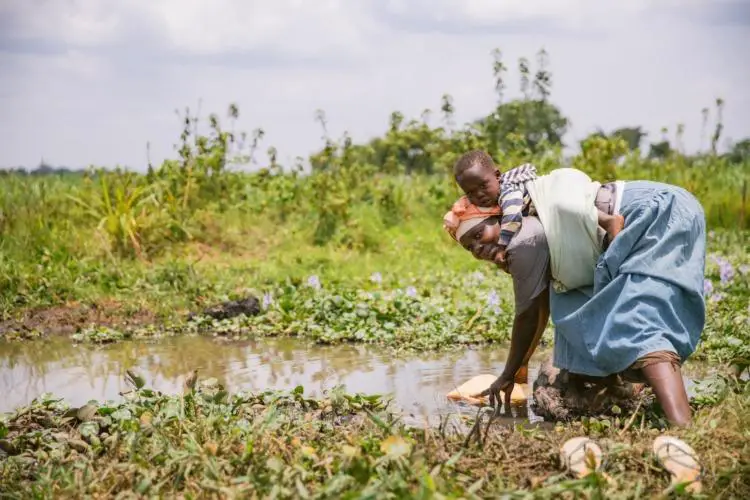
The report indicates that major cereal crops which are grown across Africa will be adversely impacted by the first half of this century.
In the worst case climate change scenario, West and Central Africa will register a reduction of yields by 13 per cent, 11 per cent in North Africa while East and Southern Africa will see an 8 per cent drop.
Millet and sorghum, which are not grown by majority of smallholder farmers who make up more than 70 per cent of the agricultural output in Africa, remain resilient and will only incur yield losses of just 5 per cent and 8 per cent respectively by 2050. Wheat and rice, which also happen to be staples, will be the most affected crops losing 12 per cent and 21 per cent respectively in yields by 2050. …
As part of the requirements under the Kenyan Act, the government additionally established an Integrated Monitoring Reporting and Verification (Integrated MRV) system and published Kenya’s National Climate Change Action Plan 2018-2022 (NCCAP). The five year plan requires the government to develop “action plans”, providing mechanisms to assist stakeholders in bringing about low-carbon climate-resilient development.
Angola boasts some of the most ambitious targets for transition to low carbon development in Africa, albeit having ratified the Paris Agreement in November 2020. Since then the country has launched a national development plan, established a climate observatory and implemented a continuous national emissions monitoring system.
In addition, Gambia is committed to reducing its GHG emissions unconditionally, by 2.4 per cent by 2025 having implemented the Sustainable Energy Action Plan in 2015, which sets out the country’s renewable energy targets and corresponding measures necessary for their achievement. It has also committed to terminating oil importation …
Water-borne illnesses are often spread through contaminated drinking water systems. Most of the contaminants are faeces and urine of sick people and animals. Another contaminant is runoff from garbage sites, landfills, sewer pipes, septic systems and industrial and residential developments.
To fight the spread of water-borne diseases in Africa, all stakeholders have to institute better sanitation measures and provide drinking water, washing and bathing facilities that promote improved hygiene. Also, water should be kept separate from waste.
In addition, extensive education programmes could help ensure that residents are aware of the proper hygiene techniques to keep their water supplies safe.…
Transport infrastructure is vital to developing countries because efficient and reliable transport networks are critical for local and international trade.
Transportation infrastructure, such as roads and railway systems, is one of the sectors most threatened by climate change. Extreme weather events such as flooding, sea-level rise, and storm surge have repeatedly wreaked Havoc on transport networks.
In Africa, extreme weather is a threat that can cause extensive structural damage. It can also accelerate the aging of infrastructure components which can lead to significant financial losses.
For instance, a recent report on Tanzania uncovered the vulnerability of the country’s transportation systems. Long stretches of road and rail networks are exposed to extreme flooding events, with growing exposure in the future.
The report estimated that worst-case disruptions to Tanzania’s multi-modal transport networks could cause losses of up to US$1.4 million per day. In addition, damage to these networks can disrupt the flow …
Over the years, various climatic disasters have occurred, notably the recent Cyclone Idai that hit the continent’s south-eastern part. Various more catastrophic weather events continue to affect the continent socially and economically. Kenya, which relies on its agricultural sector’s performance, has evidenced a sustained and growing divergence between farm production and consumption. Notable air masses like the El Nino and La Nina have had substantial negative impacts on coastal countries such as Kenya due to rising sea levels caused by changing oceanic climatic conditions.
Kenya has been forecasted to face another severe dry spell this year as a result of La Nina. La Nina, an air mass typical of cold weather, which is not ideal for rainfall, has been hitting the east coastal country nearly every five years. In 2016, 2.7 million people were affected by a hunger crisis, and the majority of them displaced. A notable concern in such …