- EAC monetary affairs committee to discuss single currency progress in Juba talks
- Transport and food prices drive down Kenya’s inflation to 5% in April
- Payment for ransomware attacks increase by 500 per cent in one year
- History beckons as push for Kenya’s President Ruto to address US Congress gathers pace
- IMF’s Sub-Saharan Africa economic forecast shows 1.2 percent GDP growth
- The US Congress proposes extending Agoa to 2041, covering all African countries
- Millions at risk of famine as fuel tax row halts UN aid operations in South Sudan
- Empowering the Future: Humanity Protocol’s Dream Play Initiative
Browsing: Ethiopia

Ethiopia plans to go ahead with it scheduled second filling of its embattled Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD). When complete, the GERD will be the largest in Africa and have the capacity to produce in excess of 6,000 MW per day.
As expected, Egypt, the historic colonial-era custodian, will not have it and along with Sudan, has called for intervention by the African Union (AU) as well as international bodies and the UN Security Council citing security reasons.
Egypt and Sudan want the UN Security Council to intervene in the GERD owing to what the Sudanese government describes as ‘its impact on the safety and security of millions of people.’
They are of the view that Ethiopia is acting of its own accord and in total disregard of the danger, its actions pose to regional stability. As such, Sudan wrote to the UN Security Council and Egypt has joined the …
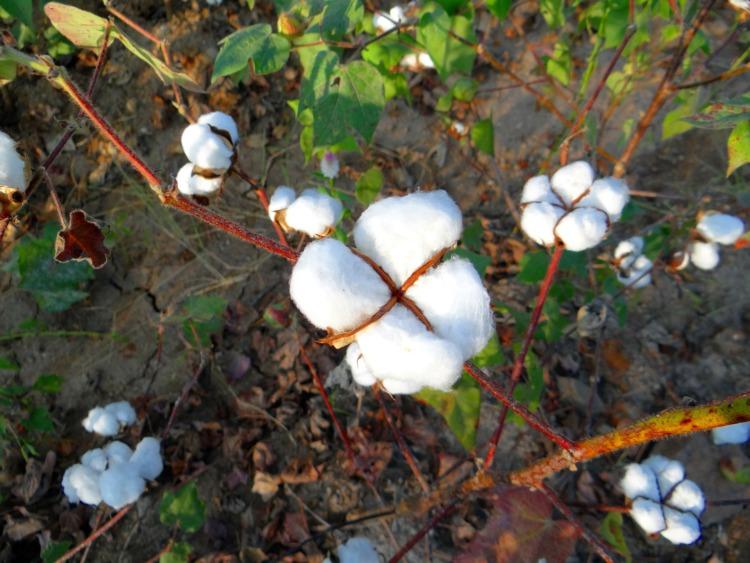
NAIROBI, Kenya, Jun 13 – East Africa Community (EAC) partner states need to exploit the potential of exporting raw cotton to international markets.
This is according to Kenya’s Principal Secretary for EAC Dr. Kevit Desai who says the region already produced 100,000 metric tonnes of cotton.
This is lower than its existing potential, which is about 400,000 tonnes.
The Principal Secretary said that EAC exports to the world market currently stand at 8 percent, adding that to increase the volume of exports, value chains such as textiles need to be promoted to boost exports.
“We need to harness science, technology, and innovation to boost exports by investing in greater capacity to produce leather and textiles, and turn a crop like pyrethrum into aerosols,” said the PS.
He added that increased investment in the leather and textile sectors would cater to the growing demand in the region for locally manufactured high-quality …
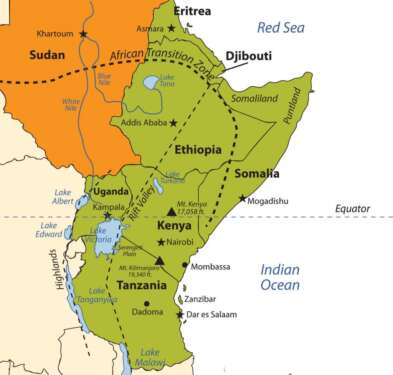
NAIROBI, Kenya, Jun 10 – The governments of Kenya and Ethiopia have this week announced the operationalization of the One-Stop Border Post (OSBP) located at the Moyale Border in Kenya’s Marsabit County.
An OSBP is a trade facilitation tool applied at land borders between two adjoining States.
It refers to the simplified and harmonised legal and institutional framework, facilities, and associated coordinated procedures and processes.
According to officials from both governments, the post is expected to enhance free movement of people and goods between the two countries, a move that will also contribute to boosting trade volumes.
Data from the statistics office indicates that Kenya’s exports to Ethiopia in 2019 were valued at USD 67 million, while Ethiopia’s exports to Kenya were valued at US$ 52.05 million.
Moyale is the only gazetted border crossing point between Ethiopia and Kenya.
Officials from Kenya and Ethiopia also expect the post to reduce …
Consider this, the first US 100 dollar bill note was issued in 1862 and the version that you know now, the Federal Reserve note featuring the US founding Father Benjamin Franklin on the foreside, was actually launched in 1914. This means that if your great, great, great grandfather happened to bury a chest full of US100 dollar bills since then, you could still today unearth it and the bill would be accepted as legal tender i.e. the same bill note is still in circulation today.
Well not quite but you get the idea. Actually, the US100 dollar bill that is used today came into circulation on July 13, 1969 and as of December 2018, the average life of a $100 bill in circulation is approximately 30 years before it is replaced due to wear. …
The Lamu Port is strategically located at the convergence of major shipping routes, saying its operationalization will open up northern Kenya to international trade, thereby fortifying the country’s position as a top economic gateway to Africa.
With one of the deep-water harbours on the east coast of Africa, Lamu Port has the potential to become a premier transhipment hub for all cargo destined for the continent. Furthermore, Lamu now joins Mombasa Port as a key entry and exit point of cargo, deep into and out of Africa’s hinterland.…
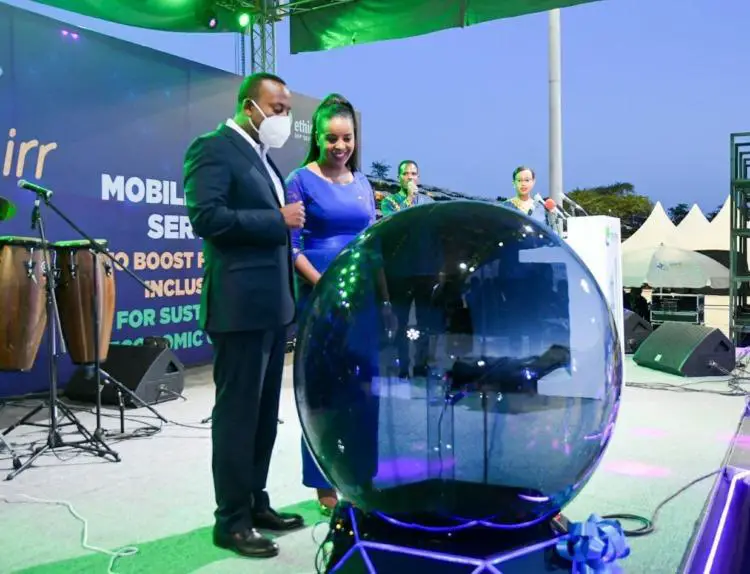
Ethio- telecom launched a service called ‘Telebirr’ as it seeks to boost growth by offering cashless transactions in Ethiopia.
Telebirr will allow ethio-telecom’s customers to send, store and receive money using their phones. The mobile money service aims to extend mobile services to areas that have been financially excluded.
With just 19 commercial banks which serve a population of 115 million, Telebirr will bridge the financial gap to those who do not have access to banks in Ethiopia.
The CEO of Ethio telecom, Frehiwot Tamiru said that within its first year of operations, the telecom plans to recruit 21 million users and 33 million in five years. She added that by the end of the five years, Ethiopia’s annual economic output of about 40 to 50 percent will be transacted on the platform.
The telecom has 1600 agents onboard already and will increase to more than 15,000 within 12 …
In 2020 gross reserves amounted to $3.1 billion which the reports said is like 2.5 months of imports and are not likely to provide a short term alternative source of development financing.
With Ethiopia expected to receive $1 billion in Eurobond in December 2024, expanding public debt in the context of large public expenditure requirements can limit the fiscal space which will lead to repayments risks. To address this challenge, the country will need to work on reforms in public finance and investments management so as to improve the efficiency of public expenditures, the report explained.
In order to contain the debt burden in the government has established the fiscal consolidation strategy ‘Home-Grown Economic Reform agenda’, which plans to expand public financing sourcing, suspend non-concessional borrowing, harness grants and concessional loan and restructure debts.…
Ethiopia has had a good run as a country these past few years and its national carrier has had an even better time in business despite the Covid-19 pandemic.
The pandemic has almost crushed many airlines but Ethiopian has remained one of the most resilient ones not only in Africa but also globally.
Ethiopian Airlines has performed so well that Airbus has awarded it for its unique agility and resilience that it displayed amid the global crisis.
Functioning under Ethiopian Airlines Group, which is the largest aviation group in Africa, the airline has managed to maintain the operation of all its fleet in a sector where its peers are operating at 10 per cent of their capability. Many airlines have gone bankrupt leading to many losing their livelihoods.
Also Read: Lessons from Ethiopian Airlines success despite pandemic
To survive the Covid-19 onslaught, Ethiopian converted its A350 passenger aircraft to …
The Moyale OSBP will help expedite the movement of goods and people across the Kenya-Ethiopia border.…
Ethiopia is incentivising investors developing minerals used in agriculture such and construction minerals.…